 |
Tenth Edition
for WACS 0.9.2
Copyright © 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 B King
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/ or send a letter to Creative Commons, 559 Nathan Abbott Way, Stanford, California 94305, USA.
Tuesday 10th May 2016
| Revision History | |
|---|---|
| Revision Tenth Edition | May 2016 |
| |
| Revision Ninth Edition | January 2013 |
| |
| Revision Eighth Edition | March 2012 |
| |
Abstract
WACS is a tool for building Adult Web Sites; it is equally suitable for managing a private collection or building a commercial web site. It has many best of breed features including dynamic filtering, model catalogs, automatic download and powerful search engine. It comes with a powerful API (application programming interface) implemented in both Perl and PHP5 languages to allow web developers to leverage it's facilities from their own programs.
This book describes the application programming interface provided by WACS, and how to utilise it from perl and Php languages. It provides an extensive introductory tutorial with a large number of worked example programs as well as a complete API reference manual. Additionally it provides a schema reference for the WACS database tables as understanding the fields available to you is central to writing programs that utilitise it. The intended audience is web developers and WACS site managers who wish to tailor an existing WACS installation to meet their precise requirements; people merely wishing to use or manage an existing WACS installation may well find the default configurations provided suffice.
The WACS source code and other documentation and support tools can all be found at the WACS website at Sourceforge and on the WACS page at Launchpad.net. The WACS demonstration site can be found at PinkMetallic.com - the site will initially be free but a charge maybe applied later to help fund additional content. Commercial add-ons and support options can be purchased from Bevtec Communications Ltd, see their website at Bevtec Communications.
Table of Contents
- I. WACS API Programming Tutorial
- II. WACS API Programming Reference
- III. WACS Database Schema
- 13. Schema Reference: Sets
- 14. Schema Reference: Assoc
- 15. Schema Reference: Idmap
- 16. Schema Reference: Models
- 17. Schema Reference: Download
- 18. Schema Reference: Photographer
- 19. Schema Reference: Tag
- 20. Schema Reference: Vendor
- 21. Schema Reference: Conn
- 22. Schema Reference: Keyword
- 23. Schema Reference: Wacsuser
- 24. Schema Reference: Attrib
- 25. Schema Reference: Notes
- Index
List of Tables
- 7.1. Simple Skin: Components
- 2. The Key WACS Modules
- 8.1. Function Summary: Core Module
- 9.1. Function Summary: User Interface Module
- 10.1. Function Summary: Standard Components Module
- 11.1. Function Summary: Identification Module
- 12.1. Function Summary: Downloading Module
- 13.1. stype: Type of Set: defined values
- 13.2. sstatus: Status of Set: defined values
- 13.3. sauto: Automatic Update of Set Allowed?: defined values
- 13.4. srating: Overall Rating For The Set: defined values
- 13.5. stechqual: Technical Quality Rating For The Set: defined values
- 13.6. svariety: Unusualness Rating For The Set: defined values
- 13.7. sformat: Format of the File(s) In The Set: defined values
- 13.8. sidlogo: Presence of Burnt-in Logo: defined values
- 13.9. sinter: Progressive or Interlaced Video Structure
- 13.10. serrors: Presence of Known Errors: defined values
- 13.11. scatflag: Generalised type of the set: defined values
- 13.12. srank: role and position of set: defined values
- 13.13. slocation: generalised description of locations: recommended values
- 13.14. sattire: generalised description of model's clothing: recommended values
- 13.15. suscattr: how to generate the 18 USC 2257 declaration: defined values
- 14.1. astatus: association status: defined values
- 15.1. istatus: idmap status: defined values
- 15.2. iactive: model activity status as this identity: defined values
- 15.3. isite: Some recommended site abbrievations: recommended values
- 16.1. mstatus: model record status: defined values
- 16.2. mrating: model rating: defined values
- 16.3. mpussy: model's normal pubic hair style: defined values
- 16.4. mflag: special marking flag for models: defined values
- 16.5. model activites flags: defined values
- 16.6. mcstatus: accuracy of home country field: defined values
- 16.7. mrace: race of the model: defined values
- 16.8. mbuild: body type of the model: defined values
- 16.9. mlabia: about the model's labia: defined values
- 16.10. mstarsign: The models astrological star sign
- 16.11. vital statistics: meanings
- 17.1. dstatus: download status: defined values
- 17.2. dtype: download set type: defined values
- 17.3. dsetflag: Suggested value for scatflag based on parsing result
- 18.1. pgender: gender of the photographer: defined values
- 18.2. pregion: geographical location of the photographer: defined values
- 18.3. prating: overall rating of photographer: defined values
- 18.4. phardness: rating of how explicit this photographer can be: defined values
- 18.5. photographer activites covered flags: defined values
- 18.6. photographer technologies used flags: defined values
- 19.1. tstatus: tag entry status: defined values
- 19.2. tflag: tag content type status: defined values
- 20.1. vcurrent: vendor existance status: defined values
- 20.2. vshow: vendor index inclusion status: defined values
- 20.3. vmdiruse et al: vendor URL auto-usuability status: defined values
- 21.1. cflag: connection type: defined values
- 21.2. cstatus: connection entry status: defined values
- 22.1. kflag: active entry status: defined values
- 23.1. ustatus: User Account Status: defined values
- 23.2. utype: User Type: defined values
- 23.3. uclass: User Class: defined values
- 24.1. atsource: attribute source: defined values
- 25.1. ntype: notes type: defined values
List of Examples
- 2.1. WACS Module Import
- 2.2. Config and Security
- 2.3. Database Connection Initialisation
- 2.4. Database Query
- 2.5. Outputing The List
- 2.6. Php: Complete Simple Program
- 2.7. Perl: Complete Simple Program
- 3.1. Modified Output Loop with Icon Code
- 3.2. Modified SQL command for more Model Info
- 3.3. New version of the loop using tables
- 3.4. Adding Model Information
- 3.5. Adding A Rating Icon
- 3.6. Calling
dberrorfor better error reporting - 4.1. The Basic SetDisp Program
- 4.2. Adding A Set Icon
- 4.3. Making Camel-Style Text Readable
- 4.4. Modified Icon Cell
- 4.5. getmodel Subroutine
- 4.6. Calling The
getmodelFunction - 6.1. WacsUI initialisation
- 6.2. Using WacsUI: describeher
- 6.3. Using WacsUI: whatshedoes
- 6.4. Using AddKeyIcons
- 6.5. Using the
iconlinkfunction - 6.6. Using the
thumblinkfunction - 6.7. Using the
contentlinkfunction
This part of the WACS Programming Guide is designed to introduce you to programming using the WACS API - examples will be given in both Perl and PHP5 dialects so you can choose to work in either language.
Chapter 1, Introduction
Chapter 2, Basics: Getting Started
Chapter 3, Using More Database Fields
Chapter 4, Set Display Routines
Chapter 5, Making The Right Selections
Chapter 6, The User Interface Toolkit
Chapter 7, Wacs-PHP: The Skins
Table of Contents
Welcome to WACS, Web-based Adult Content Server, a free software package for the management of material of an "Adult Nature" (or basically whatever euphermism for porn you prefer). It is web-based and can be used for the management of an existing collection, as a download manager, or as a back-end system for running a commercial adult web site. It is dramatically different from most other image gallery systems in that it understands photo sets and video clips as basic concepts, instead of single photographs. It also includes far more specialised tagging, source, relationship and attribute marking concepts than other more generalised systems. WACS' abilities in the areas of searching and dynamic filtering are really industry-leading in their power and flexibility.
This electronic book, the WACS Programming Guide, is designed to act both as an introduction to programming with the WACS API in either perl or PHP, and as a reference volume for both the API itself and the database schema. This book assumes you already have a basic knowledge of programming in your choosen language (PHP5 or perl5) and have some understanding of databases and in particular SQL (Structure Query Language). Some familiarity with WACS at a user level would also be a distinct advantage, and I'd strongly recommend working through the companion user guide first - who knows it might give you some ideas about neat extra features you can add to your own site. All documentation for WACS is available both within the distribution and from the WACS Web Site at Sourceforge.net.
It is important to stress that ALL of the collection management tools are implemented in Perl and the PHP interface is an optional addition to, not an alternative to, the core Wacs system which is perl based. Given the relative youth of the WACS system, php5 has been selected for the implementation to save future porting efforts as it is expected that php5 or later will be the minimum common standard by the time Wacs reaches 1.0. There is no intention to support older dialects of php at this point.
As the WACS software package is Open Source, we're always looking for contributions; if you create a site design (or prototype for one) which you don't end up using, maybe you would consider donating it to the repository of sample WACS Skins. We can always substitute our own artwork into already written web application code.
For copyright/licensing reasons, the example images feature sets from photoshoots by the main developer of WACS (Beaky) and a friend of his. These sets are available for download from the WACS demonstration site at PinkMetallic.com - CAUTION: contains adult material! Access to this site is currently free but we may have to levy a small charge in the future if refferal and donations don't reach the hoped-for amount.
Table of Contents
In this chapter we're going to talk about the basic first
steps in making use of the WACS API from your own programs. We're
going to assume that you've got a WACS server you can use up and
running; that you know where things are on it and that you have
appropriate write access to the web document tree (if you're working
in PHP) or the cgi-bin directory (if you're working in Perl). Hopefully
you'll have both some models and a few image sets known in the WACS
system to work with. For these first code examples, you could merely
load the sample model profiles we've provided in the samples
directory of the WACS distribution.
While the finished code of the sample programs featured here is
available in the samples directory of the WACS Core distribution (for
the Perl verion) or the WACS-php distribution (for the PHP5 version),
you may wish to type it in as you go along as an aid to learning how
to use the interface. If you do, we'd recommend calling this file
mysimple for perl, or mysimple.php
for PHP. For consistency, we're going to put the PHP dialect first and
then the Perl dialect in each of the examples.
The basic structure of your first WACS application will consist of five steps; these are:
import the WACS API modules
read configuration and check access rights
initialise the database connection
run an appropriate database query
retrieve records and display them
The very first step is to import the WACS API modules into your program file along with those standard modules needed to access the database. These files should be in the right location already and should just be found without any additional specification of where they are.
The same code segment implemented in perl looks like:
use Wacs; use DBI;
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The PHP interface requires an Object Handle
to use when accessing the WACS module which we're simply calling
|
The second step is to read the standard WACS configuration file to find out where everything is, and then check that this user is allowed to access the WACS system. This is a two step process, and the reading of the configuration file must be done first; otherwise WACS doesn't know where to look for the security files it needs to determine whether this user should be given access or not.
Example 2.2. Config and Security
// read the Wacs configuration files $wacs->read_conf(); // check the auth(entication and authorisation) of this user $wacs->check_auth( $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'], 1 );
and here is the same thing again in the perl dialect:
# read the Wacs configuration files
read_conf;
# check the auth(entication and authorisation) of this user
check_auth( $ENV{"REMOTE_ADDR"}, 1 );
The third step is to initialise the database connection. Since some databases require an environment variable to determine where their configuration files have been stored, this needs to be set first. Wacs provides for this and this code will create that environment variable, if needed, and then proceed to establish the database connection itself.
Example 2.3. Database Connection Initialisation
// database initialisation
// - establish environment variable
$dbienv = $wacs->conf_get_attr("database","dbienvvar");
if( ! empty( $dbienv ))
{
putenv($dbienv."=".$wacs->conf_get_attr("database","dbienvvalue"));
}
// - connect to the database
$dbhandle= DB::connect( $wacs->conf_get_attr("database","phpdbconnect") );
if( DB::iserror($dbhandle))
{
die("Can't connect to database\nReason:".$dbhandle->getMessage."\n");
}
$dbhandle->setFetchMode(DB_FETCHMODE_ORDERED);
and here's how we do it in perl:
# database initialisation
# - establish environment variable
$dbienv = conf_get_attr( "database","dbienvvar" );
if( $dbienv ne "" )
{
$ENV{$dbienv}= conf_get_attr( "database","dbienvvalue" );
}
# - connect to the database
$dbhandle=DBI->connect( conf_get_attr("database","dbiconnect"),
conf_get_attr("database","dbuser"),
conf_get_attr("database","dbpass") ) ||
die("Can't connect to database\nReason given was $DBI::errstr\n");
OK, let's just study this code for a moment. It first calls the
WACS API function conf_get_attr with the section
parameter of database as it wants database related
configuration information, and an argument of dbienvvar.
The WACS API function conf_get_attr is short for
configuration get attribute and returns the value of the
configuration file parameter of that name or it's default value. The
dbienvvar means database interface environment
variable.
A typical value for this might be something like ORACLE_HOME
which is the environment variable that Oracle 10g and 11i requires
to be set in order to find it's current configuration.
The next line of the code checks to see if we got back an actual
variable name (eg ORACLE_HOME) or an empty string (ie
nothing). If we were given a valid variable name, then we're going to need
to set it the value it should be, which again we can get from the configuration
file, this time called dbienvvalue which is short for
database interface environment value (as distinct from
the variable name we just looked up). A likely value
for this might be /usr/local/oracle. Obviously if we're
given no variable name to set, there's no point looking for a value for it!
Conversely we are assuming that having bothered to name the variable in the
configuration file, also put in a valid value for it - this code could break
if the variable name is specified but not it's value.
The second section of these code segments is to do with the
establishment of a connection to the database and is a little different
between the two versions. Both systems use a handle for the database
connection, which we call $dbhandle - imaginative name
huh? In both cases, the respective database APIs provide a
connect function which takes an argument of how to connect to
the database. The Php version takes a single argument, which is stored
in our configuration files as phpdbconnect and
includes the whole username, password and database specification in a
single lump. The Perl version asks for three: the database specification,
the username and finally the password. The configuration file knows these
as dbiconnect, dbuser and
dbpass respectively.
The final bit copes with putting out some kind of error message, at least showing the point of failure, if we are unable to establish a connection to the database. The methods are very slightly different, but the effect is very much the same between the two versions. We then just tell the PHP DB interface how we wish it to organise the returned data; the perl DBI default is pre-determined and is what we want.
![[Tip]](images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
Note that you might wish to have completed the output of the HTML header section and started the body by this point so that should the database connection fail, the error message will be visible. |
The next step in the process is to use the database connection we've established to actually make a request of the database. For now don't worry about what that request is or how we've written it - we'll come back to that topic in detail later in this chapter. Look at the mechanics of how we're issuing the request and getting back the results. What we're going to ask the database for is a list of those girls who are marked as Favourite Solo models. We chose this because both the models in our current samples directory are marked as this and so even if you only have our sample records loaded, you should find some matches.
Example 2.4. Database Query
// do db select
// 0 1 2 3
$query = "select mname, modelno, mbigimage, mimage from ".
$wacs->conf_get_attr("tables","models").
" where mflag = 'S' order by mname";
$cursor = $dbhandle->query( $query );
The method is a little different in perl in that it is seperated into two steps; as a result it looks like this...
# do db select
# 0 1 2 3
$query = "select mname, modelno, mbigimage, mimage from ".
conf_get_attr("tables","models").
" where mflag = 'S' order by mname";
$cursor = $dbhandle->prepare( $query );
$cursor->execute;
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The query structure is very similar between Php and perl apart for the two step process of validating and then seperately executing the query in perl. This is mostly down to different traditions that exist for database accesses in each language. The net result is similar in technical terms and identical in output terms |
In both cases we're putting together an SQL query that reads:
select mname, modelno, mbigimage, mimage from models where mflag = 'S' order by mname
This query asks the database to fetch the four named items:
mname, modelno, mbigimage, and mimage
from the database table called models
where the field mflag has a value of the capital letter
S and to sort the results it returns to us by the value
in the field called mname. It may not surprise you to
learn that mname is the model's name, modelno
is our reference number for her, mbigimage
is the (location of the) large size headshot of her and mimage
is the (location of the) smaller size headshot of her.
You may have noticed that the only part of this that wasn't copied
verbatim from the code is the from models bit and that
there we've used the WACS API call conf_get_attr to
get the actual name of the database table concerned from the main WACS
configuration file. This is actually important and it's strongly
recommended that you do use this form when creating SQL queries. If you
really insist on knowing why, take a look at the section on the tables
part of the wacs.cfg configuration file in the WACS configuration guide.
Once we've created the SQL query, we feed it to the database routines.
The first step is to pass in the SQL query and have the database perform
that search on the database. Once the query has been executed, we want
to pull back the matching records (or rows in database
parlence) for each model.
In both Php and Perl we're calling a routine that returns to us a single
row from the database (a single model's record in this case) each time it's
called. When we run out of records, a null return is given and our while
loop ends.
In Php, the function to do this is called using fetchRow
which returns the next row as an array of values, which we assign into the
variable $results each time.
In Perl, the function we're using is called fetchrow_array
because perl offers us a choice in the type of data we are returned and
in this case we want a numerically indexed array.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
There are other approaches to getting back the data, including
having it returned in one big lump (such as with the Php call
|
The final step is to actually generate some output from the data we've fetched from the database. We're going to do this as an unordered list in HTML, so we're going to be adding a little formating to the output as we retrieve each record.
Example 2.5. Outputing The List
print "<ul>\n";
while( $results = $cursor->fetchRow() )
{
print "<li>";
print "<a href=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("server","cgiurl");
print "wacsmpthumbs/".$results[1]."\">";
print $results[0]."</a></li>\n";
}
print "</ul>\n";
and here's the perl version...
print "<ul>\n";
while( @results = $cursor->fetchrow_array )
{
print "<li>";
print "<a href=\"".conf_get_attr("server","cgiurl");
print "wacsmpthumbs/".$results[1]."\">";
print $results[0]."</a></li>\n";
}
print "<ul>\n";
We start off by printing out the HTML instruction to start an
unordered list (<ul>) in a line on it's own. We then start a
while loop which goes through each entry until it's done them all.
Both versions use the database cursor object ($cursor)
to fetch the next record (aka row) from the database using the
fetchRow or fetchrow_array method
and assigning it into the array $results (or in perl
@results). The act of the assignment fails
when there are no more records to fetch and the while loop will terminate.
The construct here is based upon the fact that both languages have seperate
operators for assignment (=) and comparison
(== and eq) and so the code is
unambiguous (at least to the php and perl interpreters it is!).
Once inside the body of the while loop we print out the start of list
entry tag (<li>) and start in on making use of the
data. In the quest to make this example a little bit more satisfying, we've
tried to make sure this application does something vaguely useful. A simple
list of names is all well and good, but we wanted it to actually
do something! So what we've done here is to
create a link around each models name that points to her model page as
displayed by the standard WACS tools. The raw HTML to achieve this would
look like:
<a href="http://www.mywacsserver.com/cgi-bin/wacsmpthumbs/123"> Sarah</a>
So we're left with a slight problem here in that we don't know in advance (trust me on this) what the WACS server is called, we don't know what the models are called and we don't know what their numbers are. We have no idea if we have a model number 123 or not and whether she's called Sarah; but the WACS system should be able to fill in all the blanks for us.
The first part of the code merely prints out the start of the
HTML <a href="> and then we ask the WACS configuration
system what it's externally visible URL for cgi-bin programs is. We do this
using the conf_get_attr call again, telling it we want an
answer in the section server of the URL for cgi
scripts aka cgiurl. On the next line of the example
we put the name of the WACS application we want to link to, in this case
wacsmpthumbs. Since the way we tell
wacsmpthumbs what we want it to look up is to add a slash and
then the model number to the URL, we add a slash (/) on
the end and then the number.
![[Tip]](images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
You may have noticed that we added a comment on the line above the SQL select statement with 0,1,2,3 with each number above the field name in the query. This was a shorthand to ourselves to remind us what the index number in the array is for each of those database fields. |
Since the order of the fields we asked for was mname, modelno,
mbigimage and then mimage, the results in the
array will be the same - element 0 will be the mname, element 1 will be the
model number, and so on. In both cases we're dealing with a single-dimensional
array. The first field we want to go into the URL for
wacsmodelthumbs is the model number, so that
will be element 1 (not zero) therefore we write $results[1].
We then finish off the URL reference by closing the quotes (") and the
> tag.
We then want to print the model's name which will be element 0 in our arrays, put out the closing anchor tag (</a>) and then finish off the unordered line entry with the end line tag (</li>). We then print out a new line so the generated page is easier to read. The moving on to the next record will be done as a by-product of the test for the next iteration around the while loop. Once we exit the loop, we finish off the HTML unordered list.
To just finally finish it off, we need to add a few more pieces just
to make it work. For the Php version, we need to declare it as being a
php program with <?php at the very start of the file,
with a matching ?> at the very end. For perl, we
need to declare it as a perl script with the very first line being just
#!/usr/bin/perl. Additionally for perl, we need
to output the mime content type declaration so that the web browser knows
what kind of object it's being passed - this is done simply with:
print "Content-Type: text/html\n"; print "\n";
Next we need a couple of lines of HTML preamble near the beginning (as mentioned before, just before the database connection code so we could see any error message that appears):
<html> <head> <title>MySimple: Index Of Favourites</title> </head> <body>
Similarly at the end, we just need to finish the page off with the html tail piece:
</body> </html>
With all the components in place, let's review the new MySimple WACS program in it's entirety. We include the modules, initialise the configuration system, check the authorisation, connect to the database, draft the query, submit it and then loop through the results. Not really that complex now we know what each part does. Anyway here's the finished code....
Example 2.6. Php: Complete Simple Program
<?php
// MySimple - sample WACS API program (PHP5)
require_once "wacs.php";
require_once "DB.php";
$wacs = new Wacs;
// read the Wacs configuration files
$wacs->read_conf();
// check the auth(entication and authorisation) of this user
$wacs->check_auth( $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'], 1 );
// start the HTML document
print "<html>\n";
print "<head>\n";
print "<title>MySimple: Index Of Favourites</title>\n";
print "</head>\n";
print "<body>\n";
// database initialisation
// - establish environment variable
$dbienv = $wacs->conf_get_attr("database","dbienvvar");
if( ! empty( $dbienv ))
{
putenv($dbienv."=".$wacs->conf_get_attr("database","dbienvvalue"));
}
// - connect to the database
$dbhandle= DB::connect( $wacs->conf_get_attr("database","phpdbconnect") );
if( DB::iserror($dbhandle))
{
die("Can't connect to database\nReason:".$dbhandle->getMessage()."\n");
}
$dbhandle->setFetchMode(DB_FETCHMODE_ORDERED);
// do db select
// 0 1 2 3
$query = "select mname, modelno, mbigimage, mimage from ".
$wacs->conf_get_attr("tables","models").
" where mflag = 'S' order by mname";
$cursor = $dbhandle->query( $query );
// output the results
print "<ul>\n";
while( $results = $cursor->fetchRow() )
{
print "<li>";
print "<a href=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("server","cgiurl");
print "wacsmpthumbs/".$results[1]."\">";
print $results[0]."</a></li>\n";
}
print "</ul>\n";
// finish off
print "</body>\n";
print "</html>\n";
?>
Example 2.7. Perl: Complete Simple Program
#!/usr/bin/perl
#
# MySimple - Sample WACS Program (Perl)
#
use Wacs;
use DBI;
# read the Wacs configuration files
read_conf;
# check the auth(entication and authorisation) of this user
check_auth( $ENV{"REMOTE_ADDR"}, 1 );
# output the HTML headers
print "Content-Type: text/html\n";
print "\n";
print "<html>\n";
print "<head>\n";
print "<title>MySimple: Index Of Favourites</title>\n";
print "</head>\n";
print "<body>\n";
# database initialisation
# - establish environment variable
$dbienv = conf_get_attr( "database","dbienvvar" );
if( $dbienv ne "" )
{
$ENV{$dbienv}= conf_get_attr( "database","dbienvvalue" );
}
# - connect to the database
$dbhandle=DBI->connect( conf_get_attr("database","dbiconnect"),
conf_get_attr("database","dbuser"),
conf_get_attr("database","dbpass") ) ||
die("Can't connect to database\nReason given was $DBI::errstr\n");
# do db select
# 0 1 2 3
$query = "select mname, modelno, mbigimage, mimage from ".
conf_get_attr("tables","models").
" where mflag = 'S' order by mname";
$cursor = $dbhandle->prepare( $query );
$cursor->execute;
print "<ul>\n";
while( @results = $cursor->fetchrow_array )
{
print "<li>";
print "<a href=\"".conf_get_attr("server","cgiurl");
print "wacsmpthumbs/".$results[1]."\">";
print $results[0]."</a></li>\n";
}
print "<ul>\n";
# finish off
print "</body>\n";
print "</html>\n";
Our first WACS application is now complete, so copy the file into the either the web server document tree (for Php) or the web server cgi-bin directory (for perl). When you call up the URL, you should see something like this....
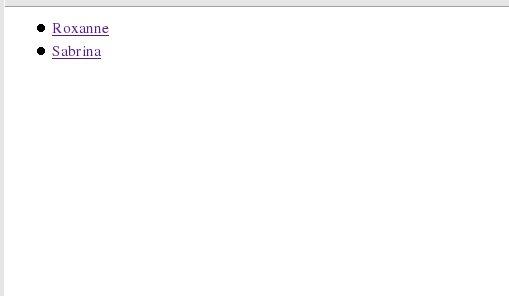
Granted it's fairly plain, but the names are in alphabetical order
and there are links on each name to that girl's model page. If you didn't
see any output, or got an error, you need to check the error log for the
server you're using. With Apache on linux, the usual location of this
is /var/log/httpd/www.mywacserver.com-errorlog or
something similar to that.
This has been a fairly long and intense chapter, but we obviously had a lot of ground to cover and we really wanted to achieve a usable program before the end of it. This hopefully we've done. We've seen how to include the WACS module and the Database interface module. We've seen how to use read_conf and check_auth to read the configuration files and check the user's credentials. We've then made multiple uses of conf_get_attr to get all of the information together we need to make a connection to the database.
After all that setup procedure, which will become a very familiar template as you program with the WACS API, we looked at creating and sending a query to the database, retrieving the results and formating those results as a simple web page. In the next chapter, we'll look at how to make use of other information stored within the database.
Table of Contents
In the simple example in the last chapter, we saw how to create a list of model's names with hypertext links on each name to that model's standard WACS model page. Obviously that's not a particularly presentable page by itself, so the next step is to add a head shot for each model to the links.
We actually already paved the way for doing this by including the two headshot image fields in the results we asked for from the SQL query - if you remember, we put:
select mname, modelno, mbigimage, mimage
Since we have the data already, all we need to do now is to add
a few extra statements to the output section to output an appropriate
image tag and we'll have included the model's headshot too. We have
a configuration attribute in the server section of
the configuration file called siteurl that tells
us where the site specific WACS web elements area can be found on the
WACS server.
Standard size
model headshots are conventionally found in the icons/
directory directly below the top level.
So all we need to do is add in a call to conf_get_attr to
get it and build the apropriate HTML img tag. In
PHP we'd write:
print "<img src=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("server","siteurl");
print "icons/".$results[3]."\" alt=\"[".$results[0]."]\">";
and in perl we'd write:
print "<img src=\"".conf_get_attr("server","siteurl");
print "icons/".$results[3]."\" alt=\"[".$results[0]."]\">";
this needs to be done just below the line that establishes the
link to the model's WACS model page, but before her name (you could
put it after if you prefer) and closing </a>.
Example 3.1. Modified Output Loop with Icon Code
while( $results = $cursor->fetchRow() )
{
print "<li>";
print "<a href=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("server","cgiurl");
print "wacsmpthumbs/".$results[1]."\">";
print "<img src=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("server","siteurl");
print "icons/".$results[3]."\" alt=\"[".$results[0]."]\">";
print $results[0]."</a></li>\n";
}
and in perl this now looks like:
while( @results = $cursor->fetchrow_array )
{
print "<li>";
print "<a href=\"".conf_get_attr("server","cgiurl");
print "wacsmpthumbs/".$results[1]."\">";
print "<img src=\"".conf_get_attr("server","siteurl");
print "icons/".$results[3]."\" alt=\"[".$results[0]."]\">";
print $results[0]."</a></li>\n";
}
We then copy up the modified version of the program and run it and we should see something like this:

The WACS database does of course carry far more information about
the model thank just her name and icons, so for the next step we're going
to look at adding a few basic pieces of information about her to each
entry. The first step is to add some additional fields to the list of
what we want returned by the SQL query. Initially we're going to add
another five fields: they are mhair, mlength, mtitsize, mnsets
and mnvideos. These database fields give
us her hair colour, length, the size of her breasts and the number of
images sets and videos we have by her respectively. The modified version
of the query looks like:
Example 3.2. Modified SQL command for more Model Info
// do db select
// 0 1 2 3 4
$query = "select mname, modelno, mbigimage, mimage, mhair, ".
// 5 6 7 8
" mlength, mtitsize, mnsets, mnvideos from ".
$wacs->conf_get_attr("tables","models").
" where mflag = 'S' order by mname");
$cursor = $dbhandle->query( $query );
in php.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
We've added a second line of comments with the element numbers within the array that the returned database field will appear in; mlength will be index 5 for instance. |
The same code in perl will look like:
# do db select
# 0 1 2 3 4
$query = "select mname, modelno, mbigimage, mimage, mhair, ".
# 5 6 7 8
" mlength, mtitsize, mnsets, mnvideos from ".
conf_get_attr("tables","models").
" where mflag = 'S' order by mname";
$cursor = $dbhandle->prepare( $query );
$cursor->execute;
The next step is to modify the display loop to include the extra details and in this case it probably makes sense to switch to using an HTML table cell to contain and manage the entry. We'll start off by simply re-writing the existing display loop to build the results into an HTML table instead - once we have that working, we'll restyle the table to include the extra fields we just added to the query. There is no actual requirement to make use of all the fields we've requested.
Lets have a look at the structure of the HTML document we're outputing here: First we need to open the new table, then each model will have her own row as we go through with the headshot image on the left and her name on the right, and finally we'll finish off the table. The HTML (minus the links) to do this will look something like:
<table> <tr> <td><img src="icons/Roxanne-1.jpg" alt="[Roxanne]"></td> <th>Roxanne</th> </tr> <tr> <td><img src="icons/Sabrina-1.jpg" alt="[Sabrina]"></td> <th>Sabrina</th> </tr> </table>
Of course the next step is to re-write the code to actually recreate
the necessary HTML; the start and end of the table simply replace the
unordered list (<ul> and </ul>
) tags outside the loop that iterates through the list of models
returned by the database. The list element (<li>
and </li>) tags get replaced by the row start
and end tags (<tr> and </tr>.
Since we're puting the headshot icon and the name in separate elements and
want a link to the appropriate model page on both of them, we need to double
up the code that creates the hypertext link to wacsmpthumbs. We then include
the icon (with alignment attributes) in a standard table tag (
<td> and the name in a heading (<th>)
table tag so it comes out in bold and is centred.
The mysimple example thus re-writen will look like:
Example 3.3. New version of the loop using tables
// output the results
print "<table>\n";
while( $results = $cursor->fetchRow() )
{
// start the HTML table row
print "<tr><td valign=top align=center>\n";
// link around the headshot image
print "<a href=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("server","cgiurl");
print "wacsmpthumbs/".$results[1]."\">";
// head shot image
print "<img src=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("server","siteurl");
print "icons/".$results[3]."\"[".$results[0]."]\"></a>\n";
// end this cell and start the next
print "</td><th>\n";
// link around name
print "<a href=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("server","cgiurl");
print "wacsmpthumbs/".$results[1]."\">";
// the name
print $results[0]."</a>\n";
// end the HTML table row
print "</th></tr>\n";
}
print "</table>\n";
// finish off
and re-writing the same function in perl gives us something like:
# output the results
print "<table>\n";
while( @results = $cursor->fetchrow_array )
{
# start the HTML table row
print "<tr><td valign=top align=center>\n";
# link around the headshot image
print "<a href=\"".conf_get_attr("server","cgiurl");
print "wacsmpthumbs/".$results[1]."\">";
# head shot image
print "<img src=\"".conf_get_attr("server","siteurl");
print "icons/".$results[3]."\"[".$results[0]."]\"></a>\n";
# end this cell and start the next
print "</td><th>\n";
# link around name
print "<a href=\"".conf_get_attr("server","cgiurl");
print "wacsmpthumbs/".$results[1]."\">";
# the name
print $results[0]."</a>\n";
# end the HTML table row
print "</th></tr>\n";
}
print "</table>\n";
# finish off
When run, this modified version of the script should produce the following:

As you can see, this has improved the layout somewhat over the previous version using just unordered list elements. Now to add those extra fields....
To display some more details about the model, we're going to span
the headshot on the left hand side over several rows, and add the model
details themselves as additional table rows on the right hand side. Our
first change therefore is to add rowspan=4 to the
options on the image container <td> tag. The
resulting php code is:
// start the HTML table row
print "<tr><td rowspan=4 valign=top align=center>\n";
// link around the headshot image
and in perl reads:
# start the HTML table row
print "<tr><td rowspan=4 valign=top align=center>\n";
# link around the headshot image
Next we add the second row which will include her hair colour and length, then a third row which will describe her breast size and the fourth row that gives the number of image sets and the number of videos we have for her.
Example 3.4. Adding Model Information
// end the HTML table row
print "</th></tr>\n";
// do the second row (her hair)
print "<tr><td>hair: ";
print $results[5]." ".$results[4];
print "</td></tr>\n";
// do the third row (her breasts)
print "<tr><td>breasts: ";
print $results[6]."\n";
print "</td></tr>\n";
// do the fourth row (her sets)
print "<tr><td>sets: ";
print $results[7];
if( $results[8] > 0 )
{
print " videos: ".$results[8];
}
print "</td></tr>\n";
and the same implemented in perl would look like:
# end the HTML table row
print "</th></tr>\n";
# do the second row (her hair)
print "<tr><td>hair: ";
print $results[5]." ".$results[4];
print "</td></tr>\n";
# do the third row (her breasts)
print "<tr><td>breasts: ";
print $results[6]."\n";
print "</td></tr>\n";
# do the fourth row (her sets)
print "<tr><td>sets: ";
print $results[7];
if( $results[8] > 0 )
{
print " videos: ".$results[8];
}
print "</td></tr>\n";
}
With these changes made, if you now run this version of the program,
which is called mysimple4 in the samples/programming
directory, you should see something like this:

There's obviously a lot more room for using many more of the fields within the model schema for further improvement of our model index, and we'll return to this subject in a later chapter (Chapter 6, The User Interface Toolkit). Before we leave the topic of models and move on to sets, we will cover just one more topic, that of adding rating icons.
One of the significant features of WACS is its ability to include various attribute icons within pages to make specific aspects and attributes easier to recognise. While many of them need some additional logic to handle their display, a few of them like the model's rating and country of origin are actually fairly simple to use. We're going to take a quick look at how we'd use the WACS API to include the rating icons before moving on to look at how we handle sets. We will return to the more complex cases later when we look at the User Interface toolkit API.
For the model's rating, we need the field called mrating
so the first step is to add this to the list of fields that
we select from the database:
// do db select
// 0 1 2 3 4
$query = "select mname, modelno, mbigimage, mimage, mhair, ".
// 5 6 7 8 9
" mlength, mtitsize, mnsets, mnvideos, mrating ".
"from ".$wacs->conf_get_attr("tables","models").
" where mflag = 'S' order by mname";
$cursor = $dbhandle->query( $query );
and in perl the change makes this section read:
# do db select
# 0 1 2 3 4
$query = "select mname, modelno, mbigimage, mimage, mhair, ".
# 5 6 7 8 9
" mlength, mtitsize, mnsets, mnvideos, mrating ".
"from ".conf_get_attr("tables","models").
" where mflag = 'S' order by mname";
$cursor = $dbhandle->prepare( $query );
$cursor->execute;
With the rating field now in the data returned to us by the
database, we can move down and update the display section to make
use of it. The first step needed is to change the rowspan
setting from 4 to 5 to accomodate the extra line of output.
// start the HTML table row
print "<tr><td rowspan=5 valign=top align=center>\n";
// link around the headshot image
and in perl...
# start the HTML table row
print "<tr><td rowspan=5 valign=top align=center>\n";
# link around the headshot image
The final step is to add the processing of the mrating field. All
WACS icons are typically stored in the glyphs/ directory
which is within the web server document tree. To find its exact URL, you
use the conf_get_attr function to retrieve the value
iconurl in the section server. Within this directory,
you will find five files called rating-1.png through
rating-5.png which look like this:
To make use of this we need to first test our data to see if we have a valid ratings value at all, then merely concatinate a string to create the necessary icon reference. In php, this will look like this:
Example 3.5. Adding A Rating Icon
print "</td></tr>\n";
// add the rating icon (if we have a value)
print "<tr><td align=center valign=top>";
if( $results[9] > 0 )
{
print "<img src=\"";
print $wacs->conf_get_attr("server","iconurl");
print "rating-".$results[9].".png\">";
print " alt=\"[".$results[9]." out of 5]\">";
}
else
{
print "no rating";
}
print "</td></tr>\n";
while the same example in perl, would look like this:
print "</td></tr>\n";
# add the rating icon (if we have a value)
print "<tr><td align=center valign=top>";
if( $results[9] > 0 )
{
print "<img src=\"".conf_get_attr("server","iconurl");
print "rating-".$results[9].".png\"";
print " alt=\"[".$results[9]." out of 5]\">";
}
else
{
print "no rating";
}
print "</td></tr>\n";
}
Once you've put in these three changes, you can run the resulting script and expect to get an output something like this:
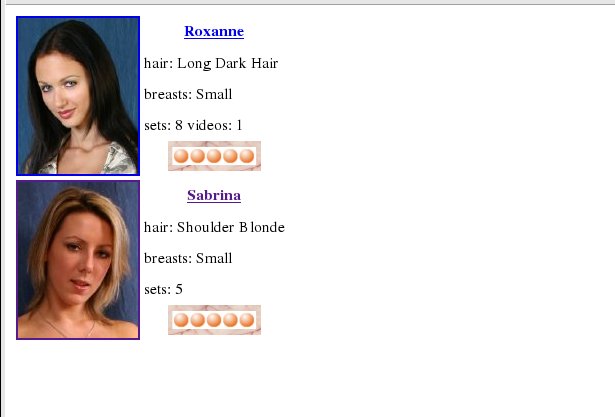
At this point we're hopefully beginning to get a rather more satisfying display of model details. Obviously there are many other tweaks we might like to add, and we'll return to some of those later on when we look at the User Interface Toolkit and the routines that provides. There is however one more thing we really should cover now - what happens when something goes wrong.
One of the most important things in good website engineering is ensuring that when things fail, it's handled gracefully with some kind of reasonable error message returned to the user, and that the event is logged properly in the system error logs. There are basically four ways in which a WACS application is likely to fail - authentication, failure to parse the configuration files, and failure to connect to the database, and failure to find the content.
The authentication failure is pretty conclusively covered by the
core WACS check_auth function and it's partners.
The parser is rather more tricky to cope with, and the
XML parse routines tend to just abort - it's also very all or nothing;
the file parses or it doesn't. Additionally once a configuration file is
in place, it's unlikely to become corrupted; if it's merely disappeared
the defaults will be used and the system will most likely have problems at
the next stage of connecting to the database. The third is connecting to
the database, which we'll deal with in a moment. The fourth, failure to
find content, doesn't result in completely blank screens and should get
reported to you quite quickly. Additionally there are so many places it
could be (raid parition, lvm volume, remote fileserver) that we can't
really do much in a general way.
Where we can get some traction is with decent reporting of database
connection problems, and this where the dberror
function comes into play. Previously, if we failed to connect to the
database we did the following in php:
if( DB::iserror($dbhandle))
{
die("Can't connect to database\nReason:".
$dbhandle->getMessage()."\n");
}
and the similar steps in perl were:
$dbhandle=DBI->connect( conf_get_attr("database","dbiconnect"),
conf_get_attr("database","dbuser"),
conf_get_attr("database","dbpass") ) ||
die("Can't connect to database\nReason given was $DBI::errstr\n");
To improve this, we're going to change this (called mysimple6 in the example code) to use the dberror function instead. This is a routine that uses named parameters, a technique we'll see a lot more of later as we use the WacsUI programming library. Basically we pass it up to five arguments or parameters, but we tell it what each one is, thus the order doesn't matter and if any of them are missing, it doesn't affect the values of the others. The dberror routine expects parameters called: header, message, error, dbuser and dbhost.
The header is to tell the routine how early
in the proceedings we are and whether we still need to start the HTML
of the web page. Setting header to y
says we do want a header added, setting it to n says
we don't. The next one, message is the message that
the end user will see. The next three are the error message returned
by the database routines, the username it was trying to use, and the
database connect string it was trying to use. Here is the code for
doing this in PHP5:
Example 3.6. Calling dberror for better error reporting
if( DB::iserror($dbhandle))
{
$wacs->dberror( array(
"header"=>"y",
"message"=>"MySimple6: Can't connect to database",
"error"=>$dbhandle->getMessage(),
"dbuser"=>$wacs->conf_get_attr("database","dbuser"),
"dbhost"=>$wacs->conf_get_attr("database","phpdbconnect")
));
}
while the same basic code in perl looks a little simpler because the parameter names don't need to be packaged up into an array before they're passed:
$dbhandle=DBI->connect( conf_get_attr("database","dbiconnect"),
conf_get_attr("database","dbuser"),
conf_get_attr("database","dbpass") ) ||
dberror( header=>'n',
message=>"Can't connect to database",
error=>$DBI::errstr,
dbuser=>conf_get_attr("database","dbuser"),
dbhost=>conf_get_attr("database","dbiconnect") );
With the error reporting improved, we'll move on to other things. We'll continue to use the short form version of the error message for brevity in the later examples, but you'll know that you probably want to actually use dberror in most cases. Next up, we'll take a look at displaying set details rather than those of models....
Table of Contents
So far we've looked at displaying the information in the models table in the database, but of course there is also the small matter of sets without which whole thing wouldn't have much point. In this chapter we're going to look at displaying details of the sets, and then towards the end of the chapter, how to tie models and sets together.
In most of these examples, we're going to use the standard WACS tools to actually display the details of the sets themselves, but you should be aware that there are several special functions within the WACS User Interface toolkit that do this rather better. We will meet these, which are called iconlink, thumblink and contentlink in a later chapter. You can of course write your own web apps or functions to do this should you wish to as well. In most cases we'll throttle the examples to only show a first few sets from the databases and assume you'll develop your own strategies for paginating and sub-dividing the sets in real world applications.
Since we're starting a new application, we'll start from scratch with the basic bones which we'll call setdisp. Much of the basic structure of this program should be getting quite familiar by now. The same five basic steps are to be found here - bring in the modules, initialise them, set up the database connection, submit the query and loop through the results outputting them.
What we're setting out to do in this script is to display a list
of the latest additions of image sets marked as being of category flag type
T which means they're solo sets involving toy usage.
This we achieve by requesting only sets of type I
which means image sets and of category flag type T.
![[Tip]](images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
The full lists of recommended values for the type and category flag can be found in the schema reference section at the back of this book in Chapter 13, Schema Reference: Sets. |
The basic format is that we once again create an HTML table with
a row for each record. There's a link on the name of the set that leads
to the standard WACS page display program wacsindex.
This takes a number of URL arguments but the one we're using here is to
prefix the set number with page which puts it into
paged display mode and appended with a .html so that
it saves correctly and in some cases will get cached. We're shrinking
the font in which it's displayed as it can be quite a long line of text
in it's stored form (but more on that topic later).
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The SQL query itself looks after the ordering of the output;
the |
Example 4.1. The Basic SetDisp Program
<?php
// setdisp - set display program
require_once "wacs.php";
require_once "DB.php";
$wacs = new Wacs;
$wacs->read_conf();
$wacs->check_auth( $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'],1 );
// start the document
print "<html>\n";
print "<head>\n";
print "<title>SetDisp - List of Sets</title>\n";
print "</head>\n";
print "<body>\n";
// connect to the database
$dbienv = $wacs->conf_get_attr("database","dbienvvar");
if( ! empty( $dbienv ) )
{
putenv($dbienv."=".$wacs->conf_get_attr("database","dbienvvalue"));
}
$dbhandle = DB::connect( $wacs->conf_get_attr("database","phpdbconnect"));
if( DB::iserror($dbhandle) )
{
die("Can't connect to database\nReason:".$dbhandle->getMessage()."\n");
}
$dbhandle->setFetchMode(DB_FETCHMODE_ORDERED);
// 0 1 2 3 4 5
$query = "select setno, stitle, stype, scatflag, simages, scodec ".
"from ".$wacs->conf_get_attr("tables","sets")." ".
"where stype = 'I' and scatflag = 'T' ".
"order by sadded desc ";
$cursor = $dbhandle->query( $query );
print "<table>\n";
$setcount=0;
while( (($results = $cursor->fetchRow()) &&
($setcount < 25 )) )
{
// start the row
print "<tr><td align=center>\n";
// create the link
print "<a href=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("apps","wacsindex");
print "/page".$results[0].".html\">";
// print out the set name
print "<font size=-2 face=\"arial,helv,helvetica,sans\">";
print $results[1]."</font></a>\n";
// end the row
print "</td></tr>\n";
$setcount++;
}
print "</table>\n";
print "</body>\n";
print "</html>\n";
?>
and implementing the same code in perl gives us:
#!/usr/bin/perl
# setdisp - set display program
use Wacs;
use DBI;
read_conf();
check_auth( $ENV{'REMOTE_ADDR'},1 );
# output the HTML headers
print "Content-Type: text/html\n";
print "\n";
print "<html>\n";
print "<head>\n";
print "<title>SetDisp - List of Sets</title>\n";
print "</head>\n";
print "<body>\n";
# connect to the database
$dbienv = conf_get_attr("database","dbienvvar");
if( $dbienv ne "" )
{
$ENV{$dbienv}= conf_get_attr( "database","dbienvvalue" );
}
$dbhandle=DBI->connect( conf_get_attr("database","dbiconnect"),
conf_get_attr("database","dbuser"),
conf_get_attr("database","dbpass") ) ||
die("Can't connect to database\nReason given was $DBI::errstr\n");
# 0 1 2 3 4 5
$query = "select setno, stitle, stype, scatflag, simages, scodec ".
"from ".conf_get_attr("tables","sets")." ".
"where stype = 'I' and scatflag = 'T' ".
"order by sadded desc ";
$cursor = $dbhandle->prepare( $query );
$cursor->execute;
print "<table>\n";
$setcount=0;
while( (($results = $cursor->fetchrow_array ) &&
($setcount < 25 )) )
{
# start the row
print "<tr><td align=center>\n";
# create the link
print "<a href=\"".conf_get_attr("apps","wacsindex");
print "/page".$results[0].".html\">";
# print out the set name
print "<font size=-2 face=\"arial,helv,helvetica,sans\">";
print $results[1]."</font></a>\n";
# end the row
print "</td></tr>\n";
$setcount++;
}
print "</table>\n";
print "</body>\n";
print "</html>\n";
When we run this set against our demonstration web server, we get the following output which is a list of the sets containing dildo use in most-recent first order.
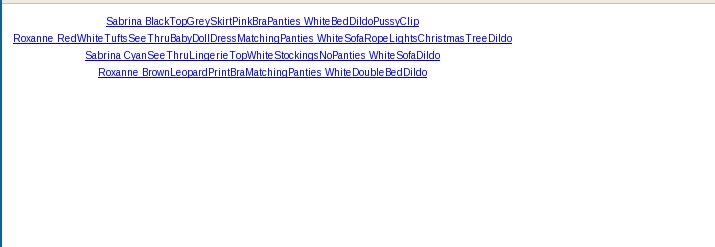
While it works and is usable, it's not exactly the greatest web
page ever, so let's try and brighten it up a little. It'd be quite nice
to be able to include an icon, and of course wacs has the infrastructure
to do this for us. In fact, it offers us three different options of what
size of icons we'd like: set, std and mini.
In this case since we're trying to get a fair number of
entries shown, we'll opt for the mini version. We
get this by calling the wacsimg command and specifying
that we'd like the mini version.
To make this happen we need to add another cell to the table with
the HTML img tag pointing at wacsimg.
As before we'll specify both align and valign
properties for this table cell.
So if we modify the code, much as we did before for the model icons, we
get the following in php:
Example 4.2. Adding A Set Icon
// start the row
print "<tr><td valign=top align=center>\n";
// create the link for the icon
print "<a href=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("apps","wacsindex");
print "/page".$results[0].".html\">";
// add the icon itself
print "<img src=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr("apps","wacsimg");
print "/mini".$results[0].".jpg\" alt=\"[icon for ";
print $results[0]."]\">";
// end cell, next cell
print "</td><td align=center>\n";
// create the link
and of course the same example in perl looks like:
# start the row
print "<tr><td valign=top align=center>\n";
# create the link for the icon
print "<a href=\"".conf_get_attr("apps","wacsindex");
print "/page".$results[0].".html\">";
# add the icon itself
print "<img src=\"".conf_get_attr("apps","wacsimg");
print "/mini".$results[0].".jpg\" alt=\"[icon for ";
print $results[0]."]\">";
# end cell, next cell
print "</td><td align=center>\n";
# create the link
and if we run the resulting program, we get something like this:

One of the design decisions taken when designing WACS was to encourage
directory names to be the same as the set names, and to make those more
usable outside of the WACS system, to make them not include spaces. Instead
the so-called Camel Technique, so named because of all
the humps in it, where an upper case letter signifies the start of each new
word. This is used along with a technique where underscores
(_) act as the transitions between the three sections of
the set name: these are:
Model or Models name(s)
Her Clothing
Location and Action
However the underscore aspect is only used in the directory name
and not in the set title (field stitle) as stored in
the database which has spaces instead. Amongst our tasks, we will need
to replace the spaces with the appropriate HTML table tags.
Fortunately we can use a regular expression to convert the
Camel-Style text back into something a little bit
more readable. This next group of changes to the code are to do exactly
that. We're going to take a slightly different approach from before as
we're not going to make the split off parts into seperate HTML table cells.
This is because that
makes both the font setting and HTML link creation much more complex - we're
merely going to insert a forced line break <br> tag
into the places where we want a new line to start. Then we're going to
break up the Camel-Style text into seperate words. We do this with:
Our first substitution is going to be to replace the spaces (the
section dividers in the stitle field) with the appropriate
HTML directives. The second and third ones actually break up the words at
the points the case changes:
Example 4.3. Making Camel-Style Text Readable
// print out the set name
print "<font size=-2 face=\"arial,helv,helvetica,sans\">";
$prettytext = $results[1];
$prettytext = preg_replace('/\s/','<br>', $prettytext );
$prettytext = preg_replace('/(\w)([A-Z][a-z])/','$1 $2', $prettytext );
$prettytext = preg_replace('/([a-z])([A-Z])','$1 $2', $prettytext );
print $prettytext."</font></a>\n";
// end the row
To implement the same functionality in perl actually uses exactly the
same regular expressions (aka regexp) but looks very
different as it's all done in assignment operations without any explicit
function call. There's no preg_replace used here.
Anyway here is exactly the same functionality in perl:
# print out the set name
print "<font size=-2 face=\"arial,helv,helvetica,sans\">";
$prettytext = $results[1];
$prettytext =~ s/\s/<br>/g;
$prettytext =~ s,(\w)([A-Z][a-z]),$1 $2,g;
$prettytext =~ s,([a-z])([A-Z]),$1 $2,g;
print $prettytext."</font></a>\n";
# end the row
With these changes in place, we can once again copy over the code and we have a much more presentable output from the program; here's an example:

Hopefully with this we've got the output presentation of the sets list looking a whole lot better than it was in the first example. There are of course many more fields within the set database that we could also make use of in our pages. We will return to them when we look at the WACS User Interface Toolkit in Chapter 6, The User Interface Toolkit. For now, before we finish our look at sets, we're just going to look at how we find the model or models featured in a given set.
One of the things that often confuses people about true relational databases is that they are unable to do a one-to-many or many-to-many relationship directly. While many so called easy-to-use databases do offer field types that purport to offer such linking, they are problematic and do not fit into any sensible logical model for how things should be structured. Worse, each vendor's implementation (those who do implement it at all) is different and incompatible. However with a sensible schema design, this limitation really isn't a problem at all.
One such instance of this need to link one-to-many is the concept of linking a set with a model within WACS. In the easy case, you'd have thought that you'd simply put the model number into one of the fields in the set schema and the job would be done. But what do you then do when you have two models featuring in a set; easy you might say - one is the main model, the other is a secondary model, so just add a second field for the additional model and put the second number there. Of course that then makes the SQL query more complex each time as you've got to check both fields before you know if a model is in a set or not. It still might work, but it's already getting cumbersome. You might discover a set first by virtue of the additional model and only afterwards identify the official primary model.
Just about every adult site we've encountered does feature at least a few sets with three models, so suddenly we're looking at a second additional model field and having to check that as well. And believe me, there are a few sites of which Sapphic Erotica comes to mind in particular where sets with three, four, five or even six models in a single set are relatively common. Simply put, adding models to the sets table just doesn't scale. So we take the proper relational database approach and add an additional schema called assoc for associations which gives us these relationships. It's a very simple schema, basically containing a primary key, a model number and a set number.
The process of finding out who is in a set becomes very simple and straight forward - you simply search the assoc table for the set number you're looking at. If we're looking for who is in set no 123, we simply use the following SQL query:
select amodelno from assoc where asetno = 123
We then merely loop through the results of the above query and each record we find is another model involved in this set. If we don't get any results returned, then there aren't any models associated with this particular set. Of course we probably want more than just the model number(s), but that too is relatively simple. Consider the following query:
select modelno, mname, mimage, mbigimage from models, assoc where modelno = amodelno and asetno = 123
This query simply retrieves the model details for each model who is
involved with this particular set, one record at a time. Due to the way
relational databases are engineered, this is actually a very quick and
efficent process. The first line of the where clause
does what is known as a relational join and establishes
the necessary connection between the assoc and
models tables necessary for what we're trying to do.
Additionally it's a very logical and elegant solution that
will cope with none, one, two, three, four or as many models as you like
within a single simple action.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Although we make use of the assoc table, we don't actually use any results from it - we don't need to - it has silently taken care of handling the connection we needed to make. |
If we go back to our example program displaying sets, we can modify it to include this activity as a sub-routine. What we're going to do is to divide the right hand side of the output into the two cells, one with the title, and the other with the model(s) featuring in the set. The icon will remain on the left. First step is to add the rowspan attribute to the left hand side cell so the icon spans it.
Example 4.4. Modified Icon Cell
// start the row
print "<tr><td rowspan=2 valign=top align=center>\n";
// create the link for the icon
and in perl, it'll look very similar:
# start the row
print "<tr><td rowspan=2 valign=top align=center>\n";
# create the link for the icon
The next step is to create a new function to handle the query
to look up the entries in the assoc table. We're going to call this
function simply getmodel and it'll take just one
argument, the set number for which we want the model(s) details. It
will return to us a potentially quite long string variable containing
all the model names that matched surrounded by a link to each model's
WACS model page.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
So long as we use a different cursor variable to the database routines we can quite happily run another query and loop through it's results while inside an outer loop looking at the results of a completely different query. This is where the whole concept of a cursor becomes really useful. |
Example 4.5. getmodel Subroutine
function getmodel ( $setno ) {
global $dbhandle;
global $wacs;
$gmresult='';
// 0 1 2 3
$modelquery="select modelno, mname, mimage, mbigimage ".
"from ".$wacs->conf_get_attr("tables","models").
", ".$wacs->conf_get_attr("tables","assoc")." ".
"where modelno = amodelno ".
" and asetno = ".$setno." ".
"order by mname ";
$modelcursor=$dbhandle->query( $modelquery );
// loop through the results
while( $modelresults = $modelcursor->fetchRow() )
{
// do we need a divider?
if( ! empty( $gmresult ))
{
$gmresult.="<br>";
}
// add the model link
$gmresult.="<a href=\"".$wacs->conf_get_attr(
"apps","wacsmthu")."/".
$modelresults[0]."\">";
// add her name and close link
$gmresult.=$modelresults[1]."</a>";
}
// return the complete string
return( $gmresult );
}
and the same code implemented in perl looks like this:
sub getmodel( $ )
{
my( $setno )=@_;
my( $gmresult, $modelquery, $modelcursor, @modelresults );
$gmresult='';
#
$modelquery="select modelno, mname, mimage, mbigimage ".
"from ".conf_get_attr("tables","models").
", ".conf_get_attr("tables","assoc")." ".
"where modelno = amodelno ".
" and asetno = ".$setno." ".
"order by mname ";
$modelcursor=$dbhandle->prepare( $modelquery );
$modelcursor->execute;
# loop through the results
while( @modelresults = $modelcursor->fetchrow_array )
{
# do we need a divider
if( $gmresult ne "" )
{
$gmresult.="<br>";
}
# add the model link
$gmresult.="<a href=\"".conf_get_attr("apps","wacsmthu").
"/".$modelresults[0]."\">";
# add her name and close link
$gmresult.=$modelresults[1]."</a>";
}
# return the complete string
return( $gmresult );
}
The final step of this process is to add into our main loop going
through the retrieved set records a call to the getmodel
function. This looks like:
Example 4.6. Calling The getmodel Function
// next right hand cell
print "<tr><td align=center><font size=-1>\n";
print getmodel( $results[0] );
print "</font></td></tr>\n";
// increment set count
and in perl this looks like
# next right hand cell
print "<tr><td align=center><font size=-1>\n";
print getmodel( $results[0] );
print "</font></td></tr>\n";
# increment set count
With these changes incorporated into the code, we now have the finished version of the setdisp program (setdisp4.php or setdisp4 in the samples directory. If we now copy this script up to the web server and run it, we should see something like this:

Once again we've gradually developed a program up to the point where it is now offering quite reasonable functionality and layout making use of the WACS programmers toolkit API. Hopefully this has given you an insight into what WACS is capable of and the basics of how to make use of it's API. In due course, we hope to have a respository of WACS skins, or mini-site scripts, which you can download and tailor to your own needs. If in the course of learning the WACS API you write some programs you'd be happy to share with others, please send them to us and we'll include them in the respository.
Table of Contents
In the last few chapters we've taken a look at how you use the WACS API and SQL commands in your code in unison to build an application using WACS. As we've gone along, we've introduced you to some of the commonly used database fields from the various schemas that form the core of the WACS environment. While there are many fields, all of which are documented in the schema reference section towards the end of this guide, there are a few that have implicit uses that you should be aware of before you start building applications in earnest.
In this chapter, we're going to look a several short code segments that should be added to the SQL queries you form to use WACS within your own programs. These code segments ensure that you don't accidentally show records that you shouldn't, have large numbers of duplicate records or fail to support some of the standard WACS facilities. All that we will discuss here are things you can choose to leave out if you know you're not going to use the related facility but in general you do need to be aware of them and it's generally good practice to support them.
We are going to be looking at three main areas of concern - hiding
model records marked as Placeholders, hiding set
records marked as Secondary and Continuation
records and supporting the preference exclusions mechanism
whereby certain types of sets are not shown to people who don't want to
see them.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Placeholder model records and preference exclusions are longstanding WACS concepts; Secondary and Continuation sets were introduced in Wacs 0.9.0 and that code is not applicable to earlier releases. Adding support for Secondary and Continuation sets requires presence of the database Schema introduced in WACS 0.8.5; using an older schema than that will cause SQL errors. |
One of the fields in the model schema is called mflag
and this is used to indicate that this particular model
record is of a special type. Mostly this is used for things like favourite
lists and is pretty unimportant to the selection process - the exception
to this is if this field has the value P which stands
for placeholder.
As you would guess from the name, Placeholder model records are not normally to be displayed - they exist to be a convenience on which to hang download and association records or to allow records to be added for new models prior to the release of any of their sets. It is therefore normal to create your SQL queries that select model records so that they explicitly do not select placeholder models.
The following SQL code segment that goes in the where clause of the SQL query will do the correct selection:
( mflag != 'P' or mflag is null )
As an example, if you were selecting all Blonde haired models you would write a query like this to get the valid models you want shown:
select modelno, mname, mflag, mrating from models where mhair = 'Blonde' and ( mflag != 'P' or mflag is null ) order by mname
There are some set records within the WACS system that you probably only want to show under a very limited range of circumstances. These are sets that are marked as Secondary or Continuation sets. Sets marked in this way offer nothing different or significant from the viewpoint of the end user but are useful to us as developers and site managers. Examples of these are different resolution versions of an existing set or a second part of a video clip that has been split into multiple smaller clips. For instance you might want to offer a reduced resolution image set for web site users to download to their mobile phones, or a choice of resolutions of a video clip.
![[Warning]](images/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
The concept of Secondary and Continuation sets was introduced
in WACS 0.9.0 - prior to that such sets were marked with a set type of
|
This mechanism is implemented through the srank
database field. This currently is defined to have three possible values or
no value - normal sets that should appear are described as primary sets
and they will have an srank of P
indicating it is a primary record. Where a record has no srank value, it
should be assumed to be a Primary
record for backwards compatibility with earlier WACS records.
In the case where a record is an alternative version of a set that
already exists, it should be given the srank of
S indicating it is a secondary record. In addition
to this, the sduplicates field for this record should
contain the set number of it's primary version and the
sduplicates field of the primary version should
point to this secondary set. Where there are three or more variants of the
same thing, this should be a circular chain taking you to the next such set
and at the final duplicate, back to the primary set.
The set administration tools do not currently support setting up a three
or more way chain of links, but the code shouldn't be broken by that
existing within the database.
The final of the three cases is that of a continuation record. These
will be given the srank of C indicating
a continuation record. This srank will only be set on the
second and subsequent set records of this conceptual chain - the first set
in a chain with continuations will be either a Primary
or Secondary set. In addition to the set being of the
Continuation type, it will have a number of other fields
set to help in navigation. The first of these is that the second such set,
eg the first continuation, will have the sprevious field
set to the set number of the first set in the sequence. If there is a second
continuation set (ie third part of the whole set), the sprevious
will be set to the number of the first set, and the snext
will be set to the number of the third (second continuation) set.
Since this is a fairly complex concept, here's a diagram to try and help you understand what is going on here:
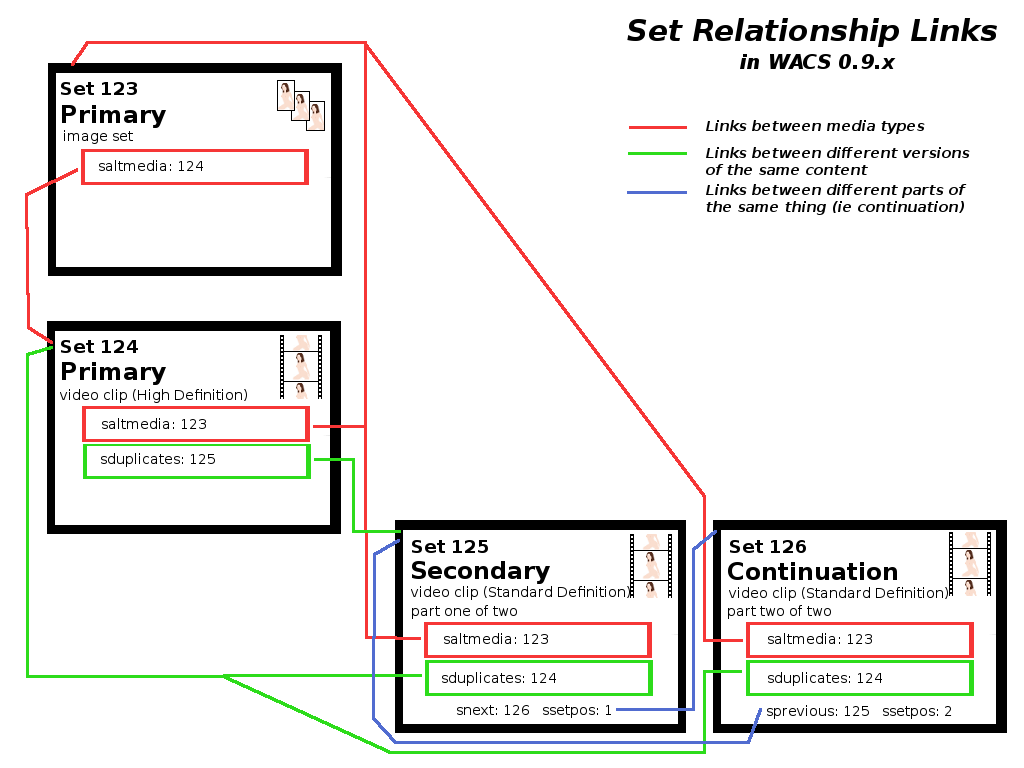
In the diagram we're dealing with four separate sets that effectively
contain exactly the same scenario with the same model in the same location.
The first of these in the diagram is set 123 which is a
straightforward image set - nothing special about it except that it does have
a corresponding video clip. It uses only one of the relationship links to
link to the best quality (and therefore choosen to be the Primary
) version of the video clip which is set 124.
This is the saltmedia link as Video is an alternative
media to a still image set.
Moving on to the video clips, note that all three of them say that
their alternative media is the single, only version of the image set.
Therefore the saltmedia on each of the videos mentions
the image set, namely set 123 as their direct alternative.
This is fine - it doesn't have to be a symetric relationship, just true!
These links are shown by the red line on the diagram.
We have three video clips and this is obviously the most complex part of the diagram and the relationships we're trying to explain. For the sake of argument we're going to say that the first video clip, set 124 is a High Definition MPEG-4 movie file weighing in at a massive 1920 x 1280 pixels and 700MBytes. It's HUGE. The other two video clips are Standard Definition WMV movie files containing the same movie at DVD resolution of 720 x 480 pixels and weighing in at 90MBytes and 82MBytes respectively. These sizes are far more appropriate for people using media players on their mobile phones, tablet computers or just simply older PCs without the power to play High Definition video properly. The movie has been broken into two approximately equal size video clips to make downloading them easier when on the move or with a limited bandwidth connection.
Starting off with the big High Definition movie clip, we can see that this is the Primary version of this set and therefore the one we want to appear in searches, new release highlights and on the simpler model pages. The other versions are no different in what they contain in terms of subject matter and the choice between them can be made once the set itself has been selected. We also don't want all three versions appearing multiply in any selection the user makes.
The first of the Standard Definition video clips contains the start of
our movie and so that's always going to be the one that anything else
refers to when looking for the smaller version. It's therefore classed as
the Secondary version and it has links back to the
primary version by way of the sduplicates link because
it contains the very same footage as the Primary version
does, just in a reduced size format. These are the green links on the
diagram.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Note that the second part of the video, namely set
126 also links back to set 124 as it's
primary as the longer complete High Definition clip contains the same
scenes as the second half of the Standard Definition clip does. Of course
if the High Definition clip was also split into two parts, the second
half of the Standard Definition clip would link via |
The final group of links on the diagram, those in blue, concern
linking together the two sequential halves of the Standard Definition
clip. Therefore set 125's snext
field says "my movie continues in set 126" and
set 126 uses sprevious to point
back to set 125 a preceeding it. In addition the
ssetpos field is set to 1, 2, 3, etc to indicate a
given clip's place within the overall movie.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
It's important to note that the |
While it's not really what we're discussing here, there are various
utility functions in the WacsStd perl module to aid and
abet in maintaining these links if you are writing your own collection
maintenance tools. Take a look at linkfromprevious
and linkrelated for more information on these.
Hopefully after the last few sections, you now understand why the Link Relations mechanism was added and how it should work. Obviously we now need to feed this back into how we write SQL code to retrieve sets. There are two main things we're going to want to do - the first is to tailor our main retrieval pages to ignore these various alternative versions, and the second is on some occasions to detect where there might be additional icons and links we need to add to our set display code.
The code to ignore Secondary and Continuation records from our normal set index selections. This can be done with this SQL code segment:
( srank not in ('C','S') or srank is null )
As an example, if you want to select Lesbian sets in a Countryside location, you'd create a query something like:
select setno, stitle, stype, srating from sets
where slocation = 'Country' and scatflag = 'L'
and ( srank not in ('C','S') or srank is null );
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
At this point we've only just started using the srank variable
and the three values of Primary, Secondary and
Continuation seem adequate. It is possible that we
might add additional values as we find a need for them - you might therefore
wish to define a variable at the top of your files - |
If you've spent a little time already familiarising yourself with WACS as a user, you may have encountered the WACS preference exclusion mechanism. We believe this is a pretty unique feature to WACS which allows a user to specify that they really don't like a certain type of set and to have those sets hidden from them by default whenever they use the WACS system. Thus if a user of a WACS site, for example, doesn't like Lesbian or Behind The Scenes sets, they can set it so those won't appear in their normal browsing or searching unless they explicitly search for them.
To enable this mechanism to work, once again you need to include a
small extra code segment in your SQL query. Once again it's a fairly
simple bracketed expression that specifies what to exclude and protects
against null (no value) as well. Taking the example
above of excluding the Lesbian (scatflag of L) and
Behind The Scenes (scatflag of B), we would add the
following code:
( scatflag not in ('L','B') or scatflag is null )
Of course, it's not quite as simple as this because we don't
actually know what a given users preference exclusions are at the time
of writing the code. We've therefore got to retrieve that information
from their authentication record, be it a lease or a permanent address-based
authentication. In earlier chapters we encountered the conf_get_attr
function that can be used to get answers from the configuration
file. There is an almost identical mechanism for getting access to the
authentication file called auth_get_attr.
To make use of the auth_get_attr function, we
need to provide it with a key with which to look up the authentication
record we want. At present we're keying this on the IP version 4 address
of the client computer to which we're talking although additional methods
are due to be added in time. When running under the Apache 2 web server,
we are provided with the address of the client computer via an environment
variable called REMOTE_ADDR. We pass this to the
auth_get_attr function with the prefix "ipv4-" to
indicate the type of address we're passing. The object we need to request
from the authentication record is called prefexcl.
Assuming that our client machine is has the IP Version 4 address of
192.168.1.136 we'd therefore effectively pass the request
to auth_get_conf as:
$exclusions = auth_get_conf( "ipv4-192.168.1.136", "prefexcl" );
Of course in fact we're not going to hard code the IP address into our Perl or PHP script, so the actual code we write will look more like this in perl:
$exclusions = auth_get_conf( "ipv4-".$ENV{"REMOTE_ADDR"}, "prefexcl" );
and in PHP it'll look like this:
$exclusions = $wacs->auth_get_attr( "ipv4-".$_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'], "prefexcl");
Once we've excuted this function call, the variable
exclusions will contain something like "L,B" -
the more observant amongst you will realise that while being what we
need to know, it's not yet phrased in a way that SQL will accept as a
list to be passed to an in() clause. We need to
quote each of the values independantly and separate them by commas.
Now that we have the preference exclusions list for our current user, we need to translate this into a form that SQL will accept as a query condition. The following code segment in perl does this for you:
$exclusions =~ s/\s//g; # remove excess spaces
$exclusions =~ s/,/','/g; # quote them
$sqlquery .= "and (scatflag not in ('".$exclusions."') or ".
"scatflag is null) ";
You will see that we're here appending to a variable called
sqlquery which is assumed to already contain the
necessary select, from and where
clauses for the search we wish to carry out. The same basic code
implemented in PHP will look like:
$exclusions = preg_replace( '/\s/','', $exclusions );
$exclusions = preg_replace( '/,/',"','", $exclusions );
$sqlquery .= "and (scatflag not in ('".$exclusions."') or ".
"scatflag is null) ";
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
One optimisation you can, probably should make, is to do this at the start of your program if you're going to write multiple database queries and place it in a global variable. The answer to the authentication file query is going to be unchanged for the time that this program will be drawing it's web page or whatever it does. |
There are of course occasions when you don't want to make use of the preference exclusions mechanism, in particular when you're handling saved searches where you assume that if the set is included within the results returned that that is what the user desires. It's also generally a good idea to indicate somewhere on the page you generate that preference exclusions have been applied when displaying this particular group of sets. While the user can change their preference exclusions at any time, it's unlikely to be that prominent that all of them will realise how to do so immediately.
Table of Contents
In this chapter, we're going to take a slightly different tack, we're going to just look at code segments you could choose to include within your application, primarily user interface components taken from the User Interface toolkit, WacsUI. This is not going to be an exhaustive review of what is available as that is covered in detail in the reference section, Chapter 9, WACS API: User Interface Module. Instead this is just a quick taster of just a few of the calls provided by the WacsUI toolkit.
So far we've been dealing with the various routines that are provided by the Core Wacs module - and these relate primarily to configuration parameters and security. There is a second module available for you to use called WacsUI, the WACS User Interface Toolkit. This concerns itself primarily with providing utility functions to ease the tasks of formatting and preparing data from the database into a form more suitable for use in web pages.
To include support for the WACS User Interface (WacsUI) toolkit within your application, you need to add the following extra lines to your code, ideally just after the Wacs core module.
and here's the perl dialect of the same activity...
use Wacs::WacsUI;
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
NB: From Wacs 0.8.6, the WacsUI module now lives in a Wacs sub-directory and so needs to be called as Wacs::WacsUI instead of just WacsUI. |
The first function from WacsUI that we're going to look at is called describeher and it is designed to take the output of the very regemented values of the model attributes fields of the database and turn them into something much more readable. Although not implemented yet this provides a good mechanism for doing other translations or providing an attribute table rather than a textual description.
Example 6.2. Using WacsUI: describeher
print $wacsui->describeher(
array( 'hair'=>$results[4],
'length'=>results[5],
'titsize'=>results[6],
'pussy'=>results[7],
'race'=>results[8],
'build'=>results[9],
'height'=>results[10],
'weight'=>results[11],
'occupation'=>results[12]))."\n";
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
We have to package up our parameter list as an array in order to pass it in Php; perl is somewhat simpler with a simple sequence of named parameters. |
print describeher(
hair=>$results[4],
length=>$results[5],
titsize=>$results[6],
pussy=>$results[7],
race=>$results[8],
build=>$results[9],
height=>$results[10],
weight=>$results[11],
occupation=>$results[12] )."\n";
The above example is based upon modifying the MySimple example program
from in the second chapter (Chapter 2, Basics: Getting Started) to add the following
extra fields into the query:
mhair, mlength, mtitsize, mpussy, mrace, mbuild, mheight, mweight,
moccupation after the mimage (with a comma of course) and before
the from clause.
As with the previous describeher,
whatshedoes is designed to make a readable sentence from a
number of fixed format database fields. In this case however, it's a
little different as the values passed in are typically either Y for
yes, or N for no, and they are translated to a text phrase based upon
what they're value is. This also means that if you're using array
subscripts to fetch the database field values you need to be careful
about positioning. Give a yes to the wrong field and the error will
not be as obvious - while “blonde breasts” would be easy
to spot, the fact that each model who did masturbation scenes was
listed as doing straight scenes would be less apparent.
For the purposes of this example, we're adding yet more fields
to the select statement in the original MySimple program shown in the
second chapter (Chapter 2, Basics: Getting Started). In this case msolo,
mstraight, mlesbian, mfetish, mtoys, mmast and
mother.
Example 6.3. Using WacsUI: whatshedoes
print $wacsui->whatshedoes( array( 'solo'=>$results[13], 'straight'=>$results[14], 'lesbian'=>$results[15], 'fetish'=>$results[16], 'toys'=>$results[17], 'masturbation'=>$results[18], 'other'=>$results[19] ) )."\n";
The same function works just the same in perl without the need for the array declaration wrapper:
print whatshedoes( solo=>$results[13], straight=>$results[14], lesbian=>$results[15], fetish=>$results[16], toys=>$results[17], masturbation=>$results[18], other=>$results[19])."\n";
Both the models and sets schemas
feature fields that contain a space seperated list of keywords that mark
certain attributes found within that set. These can be quickly turned
into a small HTML table of icons using the routine addkeyicons. The fields
suitable for use with this are scatinfo from the sets
table and mattributes from the models table. These are
passed as the first attribute; the second being the displayed size of the
icons which for the default icons would be a maximum of 48 x 48 pixels. The
function is called simply with:
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
In WACS 0.9.0 and later, |
![[Warning]](images/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
Where possible please update your existing code to pass
the |
There are three really important functions available to you within the WACS UI API which you really should get to know well. They will do a huge amount of legwork for you and are the easiest way to use the extensive content caching features built into WACS since release 0.9.1. Only iconlink existed in previous versions, and the other two thumblink and contentlink are new. In all cases these functions will automatically fall back to using the wacsimg, wacsthumb and wacszip methods if they can't do it smarter.
We're now going to take a look at WacsUI module's
most important function, iconlink. It's job is simply
to display and icon with an appropriate link around it. Sounds simple
enough, doesn't it? Unfortunately it isn't - there's a lot of work that
needs to be done relating to permissions, access methods, checking caches
and resizing which actually makes it fairly complex. The good news is
that the iconlink function will do it all for you!
The iconlink function takes quite a few arguments
which control how it works, but they are reasonably straightforward.
In most cases parameters are optional and sensible defaults will be
used instead if they are not given - obviously things like set number
and the location fields (sarea, scategory and
sdirectory) are necessary.
Example 6.5. Using the iconlink function
print $wacsui->iconlink( array( 'type'=>$setdetails[1], 'setno'=>$setdetails[0], 'sarea'=>$setdetails[2], 'scategory'=>$setdetails[3], 'sdirectory'=>$setdetails[4], 'model'=>$moddetails[1], 'resize'=> 0, 'silent'=> 'y' ))."\n";
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Note the |
The perl dialect is again very much the same:
print iconlink( type=>$setdetails[1],
setno=>$setdetails[0],
sarea=>$setdetails[2],
scategory=>$setdetails[3],
sdirectory=>$setdetails[4],
model=>moddetails[1],
resize=> 0,
silent=> 'y' ))."\n";
The thumblink function works very much the same
as iconlink does and provides a way to produce thumbnail
images from a photoset or any of a number of additional icon images
(typically thumbnails from a movie) for a video clip. It is slightly
different from iconlink in that since the cache of
set thumbnails is organised by set number and not area, category, etc,
it needs on the set number, image number and type to function.
Example 6.6. Using the thumblink function
print $wacsui->thumblink(
array( 'setno'=>$setdetails[0],
'stype'=>$setdetails[1],
'imgno'=>$imgnumber,
'resize'=>1,
'silent'=>'y' ))."\n";
And of course using it in Perl is much the same:
print thumblink( setno=>$setdetails[0],
stype=>$setdetails[1],
imgno=>$imgnumber,
resize=>1,
silent=>'y' )."\n";
The final one of the three link functions, again joining the WACS
API reportoire in release 0.9.1, is contentlink.
Once again this is similar to thumblink in not needing
the full path within the collection as the cache mechanism it refers to is
organised by set number. As with the other two members of the link family,
it falls back gracefully to the old methods of content delivery if it cannot
find a cached version of the desired content, so you can and should use it
at all times for content link delivery.
As usual we specify both the set number and the set type, plus you
also have the option by using the silent parameter as to
whether it should print out the link text it creates or merely return the
necessary text as the return variable from the function call. It's also
good practice to specify the desired name for the download file using the
archive parameter. Normally this name can simply be
taken from the sdownload field in the sets database.
If this variable is empty, it will default to set1234.zip
or set1235.wmv as appropriate.
We do usually specify the srank parameter too,
although it will function without it, to clarify the relationship of this
set to other things. The ext (for extension) is the file name extension
of this file - ie .zip, .wmv, .mov and .mpg
. As shown in the example below, passing the scodec
field from the database via the getvideoext function should
work right for videos.
The one rather odd parameter here is serve - this
specifies which type of file you would like on those occasions where there
is a choice. For some sets, the cache system holds both an original version
and a compilation or edited version comprising either the combination of a
number of seperate parts of a video clip, or a video clip with the leading
declarations trimmed so as not to disturb the viewing experience. In these
cases, if you want the compilation or edited version where are available,
you set serve to cooked and where you
want the vanilla unaltered file you set serve to
raw.
Example 6.7. Using the contentlink function
print $wacsui->contentlink(
array( 'setno'=>$setdetails[0],
'stype'=>$setdetails[1],
'srank'=>$setdetails[2],
'ext'=> $wacsui->getvideoext( $setdetails[3] ),
'serve'=>'cooked',
'archive'=>$setdetails[4],
'silent'=>'y' ))."\n";
As usual, the perl dialect version of this command is almost identical in how you call it:
print contentlink( setno=>$setdetails[0],
stype=>$setdetails[1],
srank=>$setdetails[2],
ext=> getvideoext( $setdetails[3] ),
serve=>'cooked',
archive=>$setdetails[4],
silent=>'y' )."\n";
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The content cache, unlike the icons or thumbnail caches, is NOT self-maintaining. You need to take actions to create the cached versions in the first place - please see the administration manual for more information about how to use wacscachectl to do this |
Another example of using the wacsui module can be found in the newsets.php application in the samples directory. This is a more "real world" worked example showing a new releases index page; it makes use of both the iconlink and addkeyicons functions.
Detailed documentation on each call available and how it works can be found in the API reference section Chapter 9, WACS API: User Interface Module. Another good source of examples of how to utilise these functions is to be found in the the section called “Wacs-PHP: The Simple Skin” provided as part of the Wacs-PHP API library. And of course don't forget that you can always look at how the main WACS user environment applications themselves make use of these functions.
We've now come to the end of the basic WACS API tutorial, at least for this edition of the WACS Programmers Guide. It is our intention to expand this section in future editions. Still, it has hopefully introduced you to the key concepts in making use of the WACS Programming API and given you some useful simple programs to build on when creating your own applications. The rest of this book consists of the WACS API reference manual and the WACS Database Schema Reference. If these do not provide sufficient information, please contact us via the methods listed on the WACS web site at SourceForge .
Table of Contents
In previous chapters we've mentioned that the WACS Application Programming Interface (API) is available in both Perl and PHP5. We've also mentioned that many commercial web sites will choose to design their own web pages and will make use of the extensive WACS database infrastructure and utilities via the API from such pages. Other people may simply be interested in using it to tailor the presentation of their WACS site to their personal preferences.
With the Skins project, we go a step further by providing an alternative WACS-based web site written using the Wacs API for PHP5. This can serve one of two purposes - to provide a more complex set of example programs for web designers to study in order to familiarise themselves with how the APIs are used, or it can simply be restyled and personalised to provide a turn-key porn web site quickly and easily. In due course we hope people will contribute some sample pages of their own and there may be a choice of components to make the process easier. Initially we are providing just one skin known as simple. To aid both understanding and the ease of restyling, the Simple Skin is implemented using an external cascading style sheet separate from the HTML output generated by the php programs.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The Wacs-PHP Simple Skin is still very much an under development project and only just became fully functional at 0.8.5. You can always dive in and help us make it even better! |
The provided simple skin consists of a number of small PHP5 programs and a single large style sheet shared by all the applications. The php programs are:
Table 7.1. Simple Skin: Components
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| index.php | The main menu of the simple skins site - equivalent to wacsfp in WACS itself |
| latest.php | The simple skins combined new models, new sets and new videos page - no direct WACS equivalent |
| girlie.php | The model page of the simple skins site - very loosely equivalent to wacsmpthumbs in WACS itself |
| directory.php | The Alphabetic directory of models - similiar to just one of the modes of wacsmodelthumbs in WACS itself |
| galleries.php | The index of galleries - a rather different approach from wacsshow in WACS itself. Focuses on indexing all the entries in a given top level area (sarea); to index the toplevels themselves, use movies.php below. |
| gallery.php | An individual gallery display - similiar to that produced by wacsimglist in WACS itself. |
| movies.php | A top level view of the galleries. Works for either images or videos despite the name. |
| photos.php | A photo set front page - similiar to wacsindex in info mode. |
| videos.php | The video clip version of the above. |
| search.php | The search system for the simple skin. This takes a very different approach from the search system in WACS core as it amalgamates both model and clip attributes into a single search engine. |
One of the design objectives of the Wacs-PHP skins project was to make it easy to restyle the pages to look very different without touching the code itself purely through use of Cascading Style Sheets. To this end each page has a large number of named <div> and <span> directives placed throughout the generated pages to provide a framework for this to happen.
The first of these is that every page has a standard core structure
to it which consists of three div elements with the following ids:
pagebanner for the top heading,
navigation for the menu links and
maincanvas for the content itself. They will also
always be featured in this order.
You can of course choose to make them invisible or use javascript to
toggle their visibility to make pull down menus and the like.
In addition to the core layout detailed above, there are also a
number of div classes (because they often repeat) that are set on each
type of icon that may be displayed. For set-based content, these are
normmovietile and normimagetile
for regular standard sized icons and for the smaller ones (but which are
used heavily in the simple skin) imagesettile
and moviesettile. For generic styling of the
small icons there is also a span class of miniicon
around the icon itself.
Moving on to Models, here too there are standard div wrappers around
all instances of model icons allowing them to be styled. For the normal
model headshot icon, there is a div of class modeltile
around the icon block itself, with spans of classes iconmodel
and iconmodelname around the icon itself
and the text of her name respectively. Around the large model headshot
you will find a div with the id of headshot in the
girlie.php program which is the only place that Wacs-PHP
uses the large format headshot.
There's a lot of buzz in the IT industry at the moment about dynamic content on the web - also known as Web 2.0. This is where the web page changes what it displays immediately with each selection that you make. So far we've not seen much application of the technology on adult web sites, but as we rather pride ourselves on having the capabilities of the very best, we decided to go ahead and prove we can do it with WACS. The modelsel.php application introduced in WACS 0.8.4 is the first example of this. This application simply displays various icons related to hair colour, length, breast size, pubic hair style and now in Wacs 0.8.6 we've added complexion, body type and other attributes to it. As you click on these, the page updates with a selection of headshots that match the specified criteria.
The modelsel.php application itself is fairly simplistic and it's use of the underlying AJAX architecture has been re-engineered in Wacs 0.8.6 to make more effecient use of the AJAX system. We think it's an interesting and ground breaking application and plan to do something similar for sets. We've also used it as a showcase of how realitively easy it is to integrate php-based applications into the main perl based Wacs infra-structure as it shares the look and feel of the perl based apps.
We do intend to expand on this theme in coming releases with similar dynamic search mechanisms for image sets and videos.
This is the API (Application Programming Interface) reference manual for the WACS environment. It documents the main API calls in both Perl and PHP dialects. There are now six operational modules available as part of the WACS system, plus a utility module used by the installers.
Table 2. The Key WACS Modules
| WACS Module List | ||
|---|---|---|
| name | part of | description |
| Wacs.pm | Core | the main Wacs module |
| WacsUI.pm | Core | the Wacs User Interface module |
| WacsStd.pm | Core | the Wacs Standardised Components module |
| WacsID.pm | Core | the Wacs Identification module |
| wacs.php | wacs-php | the main Wacs module, Php dialect |
| wacsui.php | wacs-php | the Wacs user interface module, Php dialect |
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
From Wacs 0.8.6 the perl WacsUI, WacsStd and
WacsId modules have been relocated into a Wacs
subdirectory for greater clarity and so now need to be used with
|
Chapter 8, WACS API: Core Module
Chapter 9, WACS API: User Interface Module
Chapter 10, WACS API: Standard Components Module
Chapter 11, WACS API: Identification Module
Chapter 12, WACS API: Downloading Module
Table of Contents
Table 8.1. Function Summary: Core Module
| function | description |
|---|---|
| read_conf | locate and read the XML based configuration file |
| check_auth | check that this is an authorised access |
| auth_error | report an authentication error and suggest remedies |
| auth_user | return the registered username for this IP |
| add_auth | add a new authentication token to access control system |
| update_auth | update the external content cache .htaccess files |
| find_config_location | try to locate the specified XML config file |
| conf_get_attr | get the requested configuration attribute |
| conf_dosubs | do substitutions for the standard wacs configuration variables |
| auth_get_attr | get the requested access control list attribute |
| dberror | produce a more helpful error page when db connections fail |
| gettoday | get today's date as a string suitable for the current DB |
| timecomps | break a date down into component parts |
| cacheloc | provide expected location of the cache files for specified set |
| vendlink | provide a link to the vendors site |
| loadattrvalues | load attribute values from the database |
| getvaluename | takes a single character flag and converts to string |
| geticonlist | gets the icon array for the specified object type |
| gettypecolour | get the prevailing colour scheme for the set type |
| divideup | make a directory name more readable |
| checkexclude | check for this file name being one to ignore/hide |
| checkindex | check for what might be an index file |
| makedbsafe | try to make the returned string safe for use in the database |
| addheadercss | add standard preamble to enable javascript menus |
| setgroupperms | set the appropriate group permissions for co-operative updating |
| treemkdir | create a tree of directories (mkdir -p equiv) |
The following pages contain the *nix style reference pages for each function call in the WACS core module. These detail what the function does, what parameters it takes, what it returns and which versions of the core library it is available in.
Name
read_conf — read Wacs core config modules
Synopsis
use Wacs;
read_conf( |
Summary
The read_conf causes the standard WACS XML
configuration file, wacs.cfg to be parsed and the
contents read into internal memory structures in the WACS module for
later use by other WACS routines. The main interface to accessing
this information is the call conf_get_attr.
read_conf is sensitive to the environment
variable WACS_CONFIG which specifies a directory
containing an alternative wacs.cfg configuration
file.
Name
check_auth — check if this IP address is authorised for access
Synopsis
use Wacs;
check_auth( | ip_address, | |
vocal_error); |
scalar ip_address;scalar vocal_error;Summary
check_auth checks whether the passed IP address
is authorised for access to this Wacs server at this time. This authorisation
may be by either permanent or lease permission based upon the calling IP
address. This IP address is specified by the first parameter to the function.
The second parameter controls what will be done about it: if the value is 0
(zero), the call will merely terminate the session by exiting the program; if
the value is 1 (one), an authorisation error HTML page will be displayed
offering the user the option to log in. In the Perl version, an additional
option of 2 (two) is available which outputs a failure icon in the case of an
expired lease and a request for an image file - this is not possible in PHP
as the content type of text/html has already been determined.
Name
auth_error — create a reasonable HTML error page with reason and link to remedy
Synopsis
use Wacs;
auth_error( | message); |
scalar message;Summary
auth_error creates a reasonable HTML error page
with reason and link to remedy if applicable (ie login page). The message
parameter will be placed in a bordered box near the bottom of the message
and can be used to convey additional information. check_auth
sets this to Sorry, your lease has expired.
when that is the case.
Name
auth_user — return the account name of the user associated with IP address
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar auth_user( | ip_address); |
scalar ip_address;Name
add_auth — add a new authentication token to the access control list
Synopsis
use Wacs;
add_auth( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| ipaddr | The IP Address of the host being authorised. |
| user | account name of the user being registered |
| type | type of registration being undertaken - currently lease
|
| role | leval of access granted currently: viewer, power
or admin |
| date | date at which this lease should expire |
| prefexcl | preference exclusions: the scatflag values not to be shown by default |
| usedirect | whether to use the usedirect function if supported by the server -
can be yes or no |
| imagepage | whether to create links to framed page or raw ones - should be
frame or raw |
| scaling | when to use image scaling - can be none, slide,
slide+page and all |
| size | size of scaled images when applicable in the format 1024x768
|
| quality | jpeg quality setting used when scaling images |
| delay | desired delay before next image in slideshow |
Name
update_auth — update the external content cache .htaccess files
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar update_auth( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| source | The comma seperated list of files to use for deriving the auth information - if not specified, defaults to the wacs.acl permanent file and the leases.acl temporary leases files. |
| dest | The comma seperated list of directories in which to place the
generated authorised IP addresses list. If not specified, it checks the
configuration variable cachelist in the security
section of the configuration file, and if that's empty, it finally uses
the values for contenti and contentv
in the fsloc section. |
| format | The desired output format - a present the only acceptable value
is apache2_htaccess (which is the default) but other
options might be available in future. |
Name
find_config_location — return the location of the requested config file
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar find_config_location( | configuration_filename); |
scalar configuration_filename;Summary
find_config_location returns the location of
the requested config file. It first checks the directory specified by
the WACS_CONFIG environment variable, and then tries
the built-in list of possible WACS configuration file locations. This
list is normally: /etc/wacs.d, then
/usr/local/etc/wacs.d and finally /opt/wacs/etc/wacs.d
. If the specified file is not found in any of these locations,
a null string is returned.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The location specified by the environment variable
|
Name
conf_get_attr — get the specified attribute from the config file values
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar conf_get_attr( | configuration_section, | |
configuration_attribute); |
scalar configuration_section;scalar configuration_attribute;Summary
conf_get_attr returns the specified attribute from
the config file or it's default value if not specified there. The WACS
configuration files are divided into a number of logical sections; the
first parameter specifies which of these is required: amongst those
defined are database, tables, fsloc, server, security, download,
colours, layout, precedence and debug. Please
see the WACS configuration guide and sample wacs.cfg files for more
information on what information is available.
Name
conf_dosubs — do substitutions for the standard wacs configuration variables
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar conf_dosubs( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| string | The string on which the substitutions should take place. |
| options | For passing in the options passed to the routine when called, will
be sustituted for #OPTIONS# within the configuration
string. |
| optdesc | For a matching description for the above, will be substituted for
#OPTDESC# within the configuration string. |
Summary
The conf_dosubs function makes substitutions
for the standard wacs configuration variables within configuration files.
It is used by various function calls within the WacsUI module including
the menu handling functions, generalised from the previous
menu_dosubs function. It is functionally compatible with
menu_dosubs so if you did make use of the original
(private) function, you can use this as a direct replacement.
In addition to substituting #OPTIONS# and
#OPTDESC# with the matching parameters, it will also substitute
the appropriate variables from the configuration files:
#BASEURL#, #CGIURL#, #ICONURL#, #SITEURL#, #WACSURL#, #WACSMAIN#,
#WACSALLM#, #WACSMODP#, #WACSMTHU# and #NEWPERIOD#.
Name
auth_get_attr — get the specified attribute from the authorisation file values
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar auth_get_attr( | ip_address, | |
authorisation_attribute); |
scalar ip_address;scalar authorisation_attribute;Summary
auth_get_attr returns the specified attribute from
the authorisation file or it's default value if not specified there. These
look ups are based on the IP address of the host - typical attributes include
the user name, the preference exclusions, the role, and the various
preference settings - see add_auth for more info.
Name
dberror — produce a more helpful error page when db connections fail
Synopsis
use Wacs;
dberror( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| header | Whether to add an HTML preamble or not: n for no,
y for yes. |
| message | The message the end-user should recieve |
| error | The error message returned from the database routines; logged in the web server error log |
| dbuser | The database user account with which the access was being
attempted, from the config file's dbuser entry. |
| dbhost | The host specification of the database that it was trying to
access, from the config file's dbiconnect entry when
using perl, and the phpdbconnect entry when using
PHP |
Name
gettoday — get todays date and various relations thereof
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar gettoday( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| format | which format to return date in (DD-MON-YYYYY or
YYYY-MM-DD) - default is native format for the current
database |
| epoch | the actual date to convert in Unix seconds since 1970 format. |
| offset | number of days different from today - assumed to be historial if postive, future if negative - thus yesterday will be 1, a week ago will be 7, tomorrow will be -1. |
Name
timecomps — return seperated time components
Synopsis
use Wacs;
array timecomps( | date_in_db_format, |
scalar date_in_db_format;Name
cacheloc — provide the expected location of the cache files for specified set
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar cacheloc( | setno, | |
| prefix, | ||
filetype); |
scalar setno;scalar prefix;scalar filetype;Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
setno | The set number |
prefix | The pathname to prefix on the destination to be checked |
filetype | The type of file to look for - can be a file type like jpg, or one
of |
Name
vendlink — provide (if possible) a link to the vendor's site for this model
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar vendlink( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| vendor | the vendor's reference (ie their vsite id) |
| page | which page to get: valid options are directory, modelpage,
bio, vidindex, vidpage, imgpage, altpage, or signup
. |
| name | the model's name |
| key | the model's key for this site |
| altkey | the model's alternative key for this site |
| setkey | the setkey if this request needs it (depends on the value of page above |
| sessionkey | the session key (if required and known). |
| modelno | the WACS model number for this request (believe me we occasionally need this) |
| setno | the WACS set number for this request (see above - this too) |
| dbhandle | current handle to the database connection |
Name
loadattrvalues — load attribute values from the database
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar loadattrvalues( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
type | specifies the context of the attribute values to be returned - the
common two are |
dbhandle | The handle to the active database connection to be used for the queries needed. |
Summary
The loadattrvalues returns an hash (or array
with alphanumeric keys) containing attribute keywords and their corresponding
icons. This replaces the older static list of attributes with a dynamic
and configurable mechanism drived from the database itself. Normally the
keys themselves are keywords and the values are the corresponding icon name.
Name
getvaluename — provide the long name for the specified value of specified type
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar getvaluename( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| object | The object you want the mapping for - see geticonlist below |
| value | The value you want mapped to it's long format (often a single character. |
Name
geticonlist — return the array of attributes to filename/long name mappings.
Synopsis
use Wacs;
hashref geticonlist( | requested_object); |
scalar requested_object;Summary
The geticonlist function returns an array/
hashref of the legal values for the requested type object. In some
cases this will be the filenames of the icon for the attributes; in
other cases it'll be the single character legal values and their
long form names. Valid requests include: models, sets, types,
media, dstatus, regions, flags, pussy, build, rank and
picon, hicon, ticon, bicon.
Name
gettypecolour — return the background colour for this type of set
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar gettypecolour( | set_type); |
scalar set_type;Name
divideup — make Camel-style text more readable and add HTML markup
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar divideup( | original_text, | |
| divider, | ||
already_small_font); |
scalar original_text;scalar divider;scalar already_small_font;Summary
The divideup function returns a more
readable version of the so-called Camel Style wording used in
creating WACS directories. It also embeds HTML directives to
try and ensure that even long entries don't take up too much space.
The first argument is the original text (typically the field
stitle from the sets database), the second (divider) is typically
the HTML break tag <br> but could be
other things like a table divider sequence </td><td>
.
The third parameter signifies whether the font in use is already small -
if set to 0 (zero), HTML tags to reduce the font size be based on using
size is -1 for long lines; if it's set to 1 (one) it'll be assumed they
were already using size is -2, and will therefore use size = -3.
As from Wacs 0.8.5, -1 is also available which suppresses the resizing
of long lines if required.
Name
checkexclude — test for being a directory file or other reserved purpose name
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar checkexclude( | filename); |
scalar filename;Name
checkindex — try to guess if this is an index image file
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar checkindex( | filename); |
scalar filename;Name
makedbsafe — try to make the returned string safe for use in the database
Synopsis
use Wacs;
scalar makedbsafe( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| string | the string of text to be considered |
| allow | characters to allow which are not normally acceptable: at present
only forward slash (/) is recognised |
| deny | characters to deny which are normal acceptable: at present any space character (space, tab, newline) given here will cause any whitespace characters to be stripped out. |
Summary
The makedbsafe function is designed to remove
characters which are unsuitable for feeding to the database. It normally
works with a default set of rules, which implicitly disallows forward slash
(but this can be explicity allowed with allow=>'/').
Similarly white space can be removed from a file name when required using
the deny option.
Name
addheadercss — prints out the header cascading style sheet preamble
Synopsis
use Wacs;
addheadercss( | css_preamble_type); |
scalar css_preamble_type;Name
setgroupperms — set group permissions to allow both command line and web management of sets.
Synopsis
use Wacs;
setgroupperms( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| target | pathname of the file or directory to update |
| group | the unix group to set permissions to (usually wacs,
can be obtained with conf_get_attr on security ->
admingroup. |
| mode | access mode that should be set - typically ug+rwX.
|
Summary
The setgroupperms function sets the group
permissions on the specified file to allow updating by both command
line tools and the web interface. This is typically done by making
all files group-writeable to the wacs group of which
both apache and the approved WACS administrative users should be members.
Name
treemkdir — Makes a descending tree of directories (equivalent to the mkdir -p command) which includes calls to setgroupperms.
Synopsis
use Wacs;
treemkdir( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| origin | The toplevel directory from which to start - this is required to already exist. |
| path | The path below the toplevel directory given above to be created (or partially created as necessary) |
Summary
The treemkdir function is the equivalent of
the -p option to the mkdir command which is not supported
by the internal mkdir call of perl. It makes each element of the path
it is asked to make if it does not already exist. This is part of the
effort to reduce the dependency on the system call to unix shell commands
within WACS. Each directory created has it's permissions set using
setgroupperms.
Table of Contents
Table 9.1. Function Summary: User Interface Module
| function | description |
|---|---|
| describeher | tries to make a sensible sentance out of model data |
| whatshedoes | describes the kind of sets this model appears in |
| addkeyicons | makes a little HTML table with the attribute icons |
| addratings | makes a little HTML table with the set ratings |
| addlinks | add standard top-of-the-page menus |
| iconlink | build a link around the icon for this set |
| contentlink | build a link to the content download (cache or wacszip) |
| thumblink | build a link to a specific thumbnail of a set image or video thumbnail |
| alsofeaturing | find and list any other models featured in this set |
| addrelicons | adds a small table containing icons from related sets |
| addconticons | adds icons from the continuation sets in a little box |
| read_menu | read the XML menu files and create menu record structure |
| menu_get_default | get the default link for the menu title |
| menu_get_title | get the menu title itself |
| menu_get_body | get the body of the menu |
| menu_get_entry | get a single entry from the menu |
| menu_get_handler | get the webapps name to handle a datatype |
| getrelated | get information on sets related to the set number given |
| getvideoext | returns the file name extension for the video format specified |
The following pages contain the *nix style reference pages for each function call in the WACS User Interface module. These detail what the function does, what parameters it takes, what it returns and which versions of the WacsUI library it is available in.
Name
describeher — tries to make a sensible sentance out of model data
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar describeher( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| name | Her name |
| hometown | Where she says she's from - might be place of birth or current home |
| country | The country she comes from |
| age | Her reported age |
| ageyear | The year in which that age was given |
| hair | The colour of her hair |
| length | The length of her hair |
| titsize | The size of her breasts |
| cupsize | The cupsize of her breasts if known |
| pussy | The usual style of her pubic hair |
| labia | description of her labia (New in 0.9.0) |
| race | Her race (in broad terms) |
| eyes | The colour of her eyes |
| distmarks | distingishing marks - easy ways to recognise her |
| build | her phyiscal build/body type |
| height | her height in centimetres (NB: field not suitable for imperial values) |
| weight | her weight in kilograms (NB: field not suitable for imperial values) |
| vitbust | her bust measurement in centimetres |
| vitwaist | her waist measurement in centimetres |
| vithips | her hips measurement in centimetres |
| starsign | her starsign if known |
| occupation | her occupation (if stated) |
| aliases | other names she's known by |
| bio | any additional biography text |
| units | override configuration file when giving units: imperial or metric |
Name
whatshedoes — describes the kind of sets this model appears in
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar whatshedoes( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| solo | does she feature in solo sets (Y, N) |
| straight | does she feature in straight sets (Y, N) |
| lesbian | does she feature in lesbian sets (Y, N) |
| fetish | does she feature in any sets flagged as fetish |
| toys | does she use toys in any of her sets |
| masturbation | does she masturbate in any of her sets |
| other | does she do any activites marked as other |
Name
addkeyicons — makes a little HTML table with the attribute icons in
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
addkeyicons( | list_of_attribute_keywords, | |
icon_size); |
scalar list_of_attribute_keywords;scalar icon_size;Name
addratings — makes a little HTML table with the ratings icons in
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
addratings( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| overall | The overall rating for the set (1 to 5) |
| variety | How unusual the content or action of the set is |
| techqual | The technical quality of the photography, lighting and set |
| size | How big the icons should be: normal or small |
| orientation | whether the table should be vertical or horizontal |
| title | display title on table: y for yes, n for no. |
Summary
The addratings function is similar to
addkeyicons in that it outputs an HTML table with
icons in. In this case, it's the ratings icons for each of the three
main set ratings: overall, variety and techqual. It can display the
table in two sizes, with or without a title and in a horizontal or
vertical orientation.
Name
addlinks — add standard top-of-the-page menus
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
addlinks( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| myname | name of the calling program |
| context | general area of the current page: possible values are
modelindex, models, search, tags, newimage, newvideo or
admin |
| title | Title of the menu (not currently used) |
| exclude | name of link to exclude (normally this apps name so it doesn't link to itself |
| mode | menu mode: either normal for old-style simple
top line menu or csshoriz to use javascript pull down
menus |
| options | optional parameter list (array) |
| optdesc | matching descriptions for the above |
Name
iconlink — build a link around the icon for this set
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar iconlink( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| type | set type value (I, V, etc) |
| setno | The set number |
| srank | The set rank - P-Primary, S-Secondary, C-Continuation |
| sarea | The toplevel area of the set |
| scategory | The middle level area of the set |
| sdirectory | The lower level area of the set |
| sformat | The format of the file (JPG,MPG,WMV,etc) |
| model | The model's name - used in the alt tag in the images |
| resize | Whether to resize or not - 0 is actual size, 1 is rescaled to standard size, 2 is rescaled to mini size |
| silent | Set this to y or yes to
suppress printed output |
| destloc | Which configuration variable or URL to use for location of link destination application - typically cgiurl for perl scripts, siteurl for php scripts, or wacsurl for wacs GUI elements (like glyphs, javascript files or stylesheets). If a full url starting http, it will be copied verbatim rather than looked up. |
| destapp | The stem of the URL to link to around the icon, something like
wacsindex/page, needs to include any parameter introducers like
page or setid= |
| destext | The extension of the URL to link to, or null, ie .html or .php.
From Wacs 0.9.0 onwards this can also be |
| prefer | Which icons to use for preference when both an official and a standard icon are available. Set prefer to "official" to use the official icon in the generated HTML. Introduced in Wacs 0.9.1, not available prior to that. |
| archive | The name of the file to be linked to when offering a download link |
Summary
The iconlink function displays the icon for
a set at the requested size surrounded by an appropriate link to the
set concerned. In WACS 0.9.1 it now returns the string that forms the
link in the same style as contentlink and
thumblink do. The default is still to print the output to
standard out as well, but this can be suppressed with the silent option.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
It is a future direction to make silent output the default for this function, so it is strongly recommended that you specify the silent flag one way or the other whenever you're updating your code. |
Name
contentlink — provide suitable link for downloading media
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar contentlink( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| setno | The set number to provide |
| stype | The type of the set to provide (I,V,etc) |
| srank | The rank of the set (P,S,C etc) |
| ext | The file name extension to use (zip, wmv, mpg, etc) |
| serve | How to serve the file: raw - the original file, cooked - edited and combined with any continuation files |
| silent | This function can either return the desired link as a string and
optionally print it out. If silent is set to y or
yes, then it will ONLY be returned and not printed. |
| archive | The name the resulting file should be delivered as - ie Jenny-12.zip. Defaults to set12345.zip as with earlier releases of Wacs. |
Summary
The contentlink function is used to create links to allow downloading of the actual content from WACS. This is designed to make a determination as to whether to simply provide a link to wacszip as in previous WACS releases, or to provide a link into the new content caching areas introduced in WACS 0.9.1.
Name
thumblink — build a link to a specific thumbnail of a set image or video thumbnail
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar thumblink( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| setno | The set number this thumbnail comes from |
| imgno | Which image number to show |
| stype | The set type (I,V, etc) |
| size | The size to show it at - std, mini, etc |
| silent | Set this to no to print link before returning |
| linkto | Link to a full frame version if required |
Summary
The thumblink provides links to thumbnailed
versions of member images of a set. For an image set, these are the scaled
thumbnails of the images within the set itself, while for videos these are
from any still thumbnails provided for the set. It will optionally add a
link around the image to any full frame or scaled displayer application you
wish to specify.
Name
alsofeaturing — look for any other models also featuring in this set
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar alsofeaturing( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| setno | The set number of this set |
| primary | The model number we already know about for this set; exclude this model from the results. Leave blank if you want all models listed. |
| staysmall | stay in a small font - if this is set to Y
font change specifications will not cause a size change. |
| destloc | the location of the destination application for the link. This
defaults to cgiurl but can be baseurl
or any of the url configuration values. |
| linkto | which wacs application to link to (assumed to be in cgi-bin). If
this ends in an equals sign (=) no slash will be added
between the application name and the modelno. This allows modelno= and
L= style arguments. |
| skipbr | tells the function not to output HTML breaks around the output it
creates. This can be first or all
as required. |
| dbhandle | current handle to the database connection |
Summary
The alsofeaturing function returns a list of
models featured in this set along with links to an appropriate WACS
application.
To aid CSS styling there is a span directive with a class of
alsofeattitle around the Featuring or Also Featuring
title output, and another with a class of alsofeatmodel
around each model link output.
Name
addrelicons — adds a small table containing icons from related sets
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar addrelicons( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| setno | The set number of this set |
| stype | The type of this set |
| sformat | The format of this set - mostly useful for videos |
| layout | How to layout the resulting output - specify table
for HTML table, div for appropriate DIVs for CSS formating.
|
| size | Size of the icons to use - mini, std, etc. |
| perrow | Specifies how many icons should be included in each row of the table when displaying continuation icons (see addconticons below) |
| destloc | Which configuration variable to use for location of link destination application - typically cgiurl for perl scripts, siteurl for php scripts, or wacsurl for wacs GUI elements (like glyphs, javascript files or stylesheets) |
| destapp | The stem of the URL to link to around the icon, something like
wacsindex/page, needs to include any parameter
introducers like page or setid= |
| destext | The extension of the URL to link to, or null, ie .html or .php.
From Wacs 0.9.0 onwards this can also be |
| destinfo | The stem of the URL to link around a link to more information,
something like wacsindex/info, needs to include any
parameter introducers like page or setid=
|
| dbhandle | Handle to the current database connection for query |
Summary
The addrelicons function returns the HTML to
generate a small table with icons with hyperlinks for duplicate and/or
continuation sets. It arranges the duplicate sets it rows, adding any
appropriate continuation icons within each row as needed. It calls
the function addconticons to produce each row of
icons.
Various optional parameters control how this HTML segment is generated.
Name
addconticons — adds a small table containing icons from continuation sets
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar addrelicons( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| setno | The set number of this set |
| stype | The type of this set |
| sformat | The format of this set - mostly useful for videos |
| layout | How to layout the resulting output - specify table
for HTML table, div for appropriate DIVs for CSS formating.
|
| size | Size of the icons to use - mini, std, etc. |
| perrow | Specifies how many icons should be included in each row of the table |
| label | Overrides the default part label if it does not contain an empty string. |
| destloc | Which configuration variable to use for location of link destination application - typically cgiurl for perl scripts, siteurl for php scripts, or wacsurl for wacs GUI elements (like glyphs, javascript files or stylesheets) |
| destapp | The stem of the URL to link to around the icon, something like
wacsindex/page, needs to include any parameter
introducers like page or setid= |
| destext | The extension of the URL to link to, or null, ie .html or .php.
From Wacs 0.9.0 onwards this can also be |
| destinfo | The stem of the URL to link around a link to more information,
something like wacsindex/info, needs to include any
parameter introducers like page or setid=
|
| dbhandle | Handle to the current database connection for query |
Summary
The addconticons function returns the HTML to
generate a small table with icons with hyperlinks for continuation sets.
Various optional parameters control how this HTML segment is generated.
It supports a similar set of onwards link specifers to iconlink to allow use with the likes of the PHP simple
skin pages if preferred.
Name
read_menu — read the XML menu files and create menu record structure
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
read_menu( | menu_filename); |
scalar menu_filename;Summary
The read_menu reads the specified menu XML
file into the internal data structures of the wacsui object. It should
be called before using any of the other menu routines. For the standard
system menus, the collection management tools look up the configuration
variable mainmenu in the layout
section which by default tells them to use the file
menu.cfg in the wacs config directory (usually
/etc/wacs.d).
You can edit the standard menu file to add your own additional menu
definitions for use in specific applications.
If your application wishes to use an alternate namespace, you could specify
an alternate menu config name, something like mysite.cfg
and also place it in the wacs config directory.
Name
menu_get_default — get the default link for the menu title
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar menu_get_default( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| name | the menus name; typically in lower case (eg navigation
) |
| caller | name of the calling application |
| exclude | applications to exclude from menus; typically the calling application itself |
| options | an array of options to be substituted. |
| optdesc | a matching array of descriptions |
Name
menu_get_title — get the menu title itself
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar menu_get_title( | ...); |
Name
menu_get_body — get the body of the menu
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar menu_get_body( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| name | name of the menu concerned |
| caller | name of the program calling it |
| exclude | name of program to exclude from menus |
| options | array of options to use |
| optdesc | array of matching descriptions for the options above |
| isarea | hashref/array of image-based sarea values |
| vsarea | hashref/array of video-based sarea values |
| mflags | hashref/array of model flags |
| vsites | hashref/array of vendor codes and names |
| pre | prefix for generated entries (eg <li><a href=\"
) |
| intra | middle section for generated entries (eg \">)
|
| post | postfix for generated entries (eg </a></li>
) |
Name
menu_get_entry — get a single entry from the menu
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar menu_get_entry( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| name | name of the menu concerned |
| caller | name of the program calling it |
| entry | hashref/array of the current entry object from menu tree |
| options | array of options to use |
| optdesc | array of matching descriptions for the options above |
| isarea | hashref/array of image-based sarea values |
| vsarea | hashref/array of video-based sarea values |
| mflags | hashref/array of model flags |
| vsites | hashref/array of vendor codes and names |
| pre | prefix for generated entries (eg <li><a href=\"
) |
| intra | middle section for generated entries (eg \">)
|
| post | postfix for generated entries (eg </a></li>
) |
Summary
The menu_get_entry takes an individual menu
entry (which may result in multiple menu entry lines) and processes it
into a string that is returned. It is available seperately as it can be
called with custom parameters via options and optdesc to do specific
non-standard parameters.
All the usual substitions are available including a special one called
#NEWPERIOD# which provides a text representation of
the current value of the layout->newperiod variable.
Name
menu_get_handler — get the webapps name to handle a datatype
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar menu_get_handler( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
for | The type of data this is a handler for; usually this will be the
table name, eg models but it can be any arbitary
name. |
options | This is the primary key to be passed to the application specified in the lookup. |
Summary
The menu_get_handler function is there primarily
to let you find the applications that mesh best with the menu tree currently
being used. You pass to the function the table or activity name and the
primary key (or other lookup parameter) and it will return the preferred
application to
handle that type of link for this menu/look and feel in use. If the menu
configuration file does not include a specification of the handler for any
of the standard database tables, the default Wacs application will be given
as the reply. A null reply will be indicated by a single character reply
of just the hash character.
| Some Common Names |
|---|
| mainmenu |
| models |
| photographer |
| preferences |
| slideshow |
Name
getrelated — get information on sets related to the set number given
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar getrelated( | ...); |
Parameters
| paramter | description |
|---|---|
| relation | gives the type of relation we're looking for. Available options
are |
| stype | gives the type of the set we're dealing with - ie I
or V. |
| setno | the set number to start from - most likely the first in the set but not necessarily. The progression will only be forwards however. For alternative media, this can be expected to be the start point that we don't want given back to us. |
| alternative | This is the first alternative number to look for when looking for alternative media. The chain continues until we get back to the set number given. |
| duplicates | This is the first number of a duplicate set to look for when finding alternatives. If you don't specify this option, the search will start with the set itself - sometimes this maybe what you want. |
| dbhandle | the database handle to use for submitting queries to the database |
Summary
The function getrelated provides a tool for
finding a sequence of related sets based on the requested type of relation
to look for and the set number given. If the relation specified is
continuation it will return an array starting with
the set itself in element zero and will then follow links in
snext to find the chain of related sets and each subsequent
element will be the setno of the next set in the continuation chain.
If the relation specified is altmedia it will
return an array of all sets of other media types related to this set, but
not the set's own details.
Name
getvideoext — returns the file name extension for the video format specified
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
scalar getvideoext( | format); |
scalar format;Parameters
The getvideoext takes the name of the video
format (ie MPEG, QuickTime, etc) as stored in the sformat
database field.
Table 10.1. Function Summary: Standard Components Module
| function | description |
|---|---|
| masthead | creates a top-of-the-page summary for any page handling set |
| modelmast | creates a model-focused top-of-the-page summary |
| modelheads | adds the icons with links for model(s) specified |
| findmodel | creates a table and choice box for models with a given name |
| findrecentsets | creates rows in a table managed form with pull-down menus containing details of recently added sets |
| findrecentmodels | creates rows in a table managed form with pull-down menus containing
details of recently added models and a search box to be fed to
findmodel |
| modelheadshot | creates a model headshot icon and basic info table contents |
| getgallery | work out the next available gallery slot when in gallery layout mode |
| callframe | create a suitable URL for page based navigation of the specified set |
| foundatsite | return a list of other sites where this model can be found |
| kwscore_reset | resets the keyword scoring system back to defaults |
| kwscore_process | process the provided string looking for keywords |
| kwscore_get | get the specified result from the processing of the strings provided previously |
| getcontinfo | get various pieces of information from the named set relevant for a continuation set |
| linkfromprevious | updates a previous set in a continuation with details of set just added |
| linkrelated | updates a related set with details of the set just added - works for duplicates and alternative media |
| removedups | remove duplicates from an attribute string |
| removeconflicts | remove items that contradict the set attributes from the model attributes |
| addassoc | Add a new model/set association record |
| related_set_info | Create a popup menu of possible related sets |
| wacsblogtodb | write a new blog entry into the specified database table |
| alloc_nextkey | Work out the next primary key value for the specified database table |
The WacsStd module contains standard components for building the standard WACS collection management tool interface. Since all these tools are written in perl, this module is only implemented in perl.
Name
masthead — top of page banner for set-based apps
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
masthead( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| setno | The set number |
| stype | The set type (single letter database format) |
| scatinfo | The attributes for the set |
| scatflag | The set type flag (single letter database format) |
| stitle | The assigned set title, aka standard description |
| sofftitle | The official title (usually from original site) |
| sarea | Toplevel directory entry |
| scategory | Middle level directory entry |
| sdirectory | lowest level - actual holding directory (filename for videos) |
| simages | Number of images in the set |
| sindexes | Number of index images for the set |
| saspect | aspect ratio (mainly for videos) |
| sformat | file format for this set (.jpg, .png, .mov, .wmv etc) |
| sdurhrs | video or DVD scene duration - hours value |
| sdurmin | video or DVD scene duration - minutes value |
| sdursec | video or DVD scene duration - seconds valus |
| sphotog | photographer reference code (references pref in photographer) |
| sfoundry | organisation where the set came from |
| modelno | associated model number |
| downloadno | associated download record number |
| useicon | when working with a set number 0, attempt to get an icon by asking for a thumbnail of the first image |
| addlinks | add set browsing links to the masthead centre section |
| width | make the masthead table the specified width only |
| dbhandle | the current database handle object |
Name
modelmast — creates a model-focused top-of-the-page summary
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
modelmast( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| mname | The model's name |
| modelno | The model's primary key (model number) in the WACS database |
| modelicon | The path relative to siteurl to the model's
icon - can be the big or small icon or even body image. |
| mrating | The model's rating out of five |
| mattributes | The model's attribute list as used in addkeyicons |
| mcountry | Which country the model is from for the flag |
| linkoptions | Pre-formatted HTML string of the links you want to appear as alternatives to the current page - as used in the model page for other sizes of model page. This will appear in the right hand side of the masthead, towards the bottom. |
| generalinfo | Pre-formatted HTML string used for the upper part of the left hand box below the model's name. This is used for basic statistics and info in the model page. |
| shedoes | This is the preformatted HTML string for the middle part of the left had box below the model's name. This is used for what types of sets this model appears in in the model page. |
| currentexcl | This is another preformatted HTML string - this one is used to highlight exceptions and unusual circumstances. In the model page, this indicates if exceptions or filtering is active. Appears towards the bottom of the left hand box below the model's name. |
| descher | This is an HTML formatted string to go in the right-hand box below
the model's name. In the model page, this is usually the output from the
describeher function. |
| iconsize | The size of icons to use when displaying attributes, etc |
| dbhandle | The handle to the current database communication channel. |
Summary
modelmast is similar to the
masthead function except that it is focused on
the model rather than the set. Originally developed for use on the main
WACS model page, it has now become a freestanding API call that can be
used from a number of applications. It includes a number of parameters
that take pre-formatted HTML strings to increase the flexibility of how
it can be used. All will be housed within a td
element of an HTML table rendered in the configured masthead colours.
Name
modelheads — adds the icons with links for model(s) specified
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
modelheads( | lookup_method, | |
| set_number, | ||
dbhandle); |
scalar lookup_method;scalar set_number;scalar dbhandle;Summary
The modelheads function was originally written
as part of the implementation of masthead but has
broader uses. It provides a table of a model (or group of models) headshots
with ratings and name. The lookup_method can
be one of byset (where it's the models featured in the
specified set number) or byno (where the second
argument is the model number rather than the set
number). The default option in other cases is any models who've been
added today - it is recommended you specify bydate
and pass the date for this option.
Name
findmodel — creates a table and choice box for models with a given name
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
use Wacs::WacsUI;
findmodel( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| mname | the model name or beginning of the name to look for |
| offeralt | Whether to offer an alternative choice or not: y or n |
| offervalue | What the value returned for the alternative should be, eg
next |
| offercapt | What the caption for the alternative value should be |
| incsubmit | Whether to include a submit button or not: y or n |
| dbhandle | pointer to the currently active database handle |
| cgihandle | pointer to the currently active CGI object |
Summary
The findmodel function takes the name of a model
and searches the database for who it might concievably be. It checkes the
model's name, her aliases and the name from each of her ID map entries. It
presents a headshot, description, and a radio button to allow her to be
choosen. It can optionally offer an additional radio button for another
purpose. The choosen model's number or next will be
returned in a CGI variable called modelno.
Name
findrecentsets — creates rows in a table managed form with pull-down menus containing details of recently added sets
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
findrecentsets( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| offset | the number of days in the past to consider as recent. Defaults to
the current value of layout->newperiod if not specified.
|
| default | the default value for the set number if known. |
| dbhandle | pointer to the currently active database handle |
| cgihandle | pointer to the currently active CGI object |
Summary
The findrecentsets function creates rows in a
table managed form with pull-down menus containing details of recently
added sets. The method selected by the user for specifying their
response will be stored in a CGI variable called setmeth
which will have a value of one of specify,
image or video.
If their response is specify
the setno will be in a CGI variable called spec_setno.
If their response is image the setno will be in a CGI
variable called recent_img and for video
it'll be in recent_vid.
Name
findrecentmodels — creates rows in a table managed form with pull-down menus containing
details of recently added models and a search box to be fed to
findmodel
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
findrecentmodels( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| offset | the number of days in the past to consider as recent. Defaults to
the current value of layout->newperiod if not specified.
|
| default | The default model number if known. |
| dbhandle | pointer to the currently active database handle |
| cgihandle | pointer to the currently active CGI object |
Summary
The findrecentmodels function creates rows in
a table managed form with pull-down menus containing details of recently
added models and a search box to be fed to findmodel.
The method selected by the user for specifying their response will be
stored in a CGI variable called modmeth
which will have one of these values: specify,
recent or search.
If their response is specify the modelno will be in a
CGI variable called spec_modelno.
If their response is recent, the modelno will be in a CGI
variable called recent_mod. If the value is
search the findmodel function
should be called passing the CGI variable search as
the mname parameter.
Name
modelheadshot — creates a model headshot icon and basic info table contents
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
modelheadshot( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| modelno | The model number - that is our model number for her. |
| name | The model's name that we're looking for - thus if we know the model as Jedda, but know she's known as Jana elsewhere, we'd put Jana here to build up a link along the lines of "Known as Jana at KPC" in the id description field. |
| howcome | How we came by this model - this can be S as
the result of a name search or I if we're displaying
her ID details for a specific site. |
| where | The site id or short name for where we found this model called this name |
| key | The model's key on the site we're talking about if specified. |
| dbhandle | pointer to the currently active database handle |
Name
getgallery — get the next available slot in the named gallery
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
scalar getgallery( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| which | Specifies which area to substitute in - can be either scategory (middle level) or sdirectory (lower level). |
| stype | stype of the set concerned: typically I for image set, V for video. |
| sarea | Top level area in which to search for the next available gallery slot |
| scategory | The middle level directory entry (can be either simply specified or the
subject of the substitution). This should include the variable pattern
given in substitute below, as in gallery#NEXT#. |
| sdirectory | The lower level directory entry (if needed, otherwise blank). |
| substitute | The string to be substituted with the value determined by the
routine. Typically this will be something like #NEXT#.
|
| dbhandle | The Perl DBI handle to the current database |
Summary
The getgallery function returns the appropriate
string for the next available slot in the gallery in the specified section.
It can return either an scategory or sdirectory variable as requested via
the which parameter. It is used to work out the placement of new sets
within a gallery structure. What the next usable gallery is is determined
by reference to the layout attribute
setspergallery in the configuration file or the default value
(usually 20) if not specified. Please see the configuration manual for
more details on this configuration attribute.
Name
callframe — create a suitable URL for page based navigation of the specified set
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
scalar callframe( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| imgprefix | which size prefix to use - mini, std, set etc - when calling wacsimg |
| setno | The set number we're displaying |
| curimg | What should be the current image number we're starting from |
| maximg | How many images there are in this set |
| models | Models specified as name, "-", model number. Comma seperated if there's
more than one. For example: Jane-231,Sara-78 |
| pagemode | If this is |
| appstem | This is the configuration menu to use with |
Summary
The callframe function returns a suitable URL
for accessing the wacsframe single image framing application
with the appropriate parameters to properly integrate it into the particular
WACS environment from which it's called. The intended use of this function
and it's interoperation with the standard wacs tools is really best understood
by examining it in use by the Wacs-PHP simple skins. These show how this
can be used to pass customization information between the various applications.
Name
foundatsite — return a list of other sites where this model can be found
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
scalar foundatsite( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| modelno | The model number we want the results for |
| sitedesc | How the site should be described - initially only ref
is accepted. In due course, other options like
shortname should also be acceptable. |
| linkdest | The application to link to - for instance wacsmodt |
| itemsep | How to seperate the items - ie , (comma, space) or
more complex HTML like >/li<>li< to make them
list items |
| textcolour | The colour to use for the link - typically a call to
conf_get_attr("colours","mastheadforeground"). |
| dbhandle | the database session object pointer |
Name
kwscore_reset — resets the keyword scoring system back to defaults
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
kwscore_reset( | scope); |
scalar scope;Summary
The kwscore_reset function resets the currently
built attributes table. It is possible to run the kwscore_process
function several times with different fields from the database
and so it does not naturally reset the internal table of results - this call
provides that facility and should always be called before each new set to
consider. The scope parameter is currently ignored but
may in future modify the behaviour.
Name
kwscore_process — process the provided string looking for keywords
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
kwscore_process( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| string | the string to be processed against the keyword database |
| dbhandle | the database session object pointer |
Summary
The kwscore_process function allows you to
submit a string to the keyword scoring system for consideration. It's
scores will be stored allowing both retrieval of results and modification
of those results by subsequent invocation of the kwscore_process
with alternative strings. It is perfectly possible to consider
both the title (field stitle) and the official title
(field sofftitle) if that is appropriate. It could also
be run on the description of the set if that is present.
Name
kwscore_get — get the specified result from the processing of the strings provided previously
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
kwscore_get( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| what | which result you are requesting: valid ones are: cat, loc,
det, attr or other. |
| default | a default value you want returned if nothing is found for this request |
Summary
The kwscore_get function retrieves the results
from any kwscore_process calls made since the last
kwscore_reset. The what argument
specifies what to return:- cat returns a category
flag (scatflag etc.), loc returns
a location (slocation), det returns
a detailed location (slocdetail, attr
returns the attributes (scatinfo and other
is available for future expansion.
Name
getcontinfo — get various pieces of information from the named set for the continuation
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
scalar getcontinfo( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| setno | The set number for which the information is required. |
| dbhandle | Database handle for the current connection to the database. |
Name
linkfromprevious — updates a previous set in a continuation with details of set just added
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
linkfromprevious( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| setno | The set number for set just added. |
| previous | The set number for the older set now being referred to as the previous one in a connection series. |
| setpos | The position of this set in a sequence of sets (must not be 1!). |
| dbhandle | Database handle for the current connection to the database. |
Name
linkrelated — updates a related set's duplicates or alternative media links with details of a set just added
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
linkrelated( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| setno | The set number for set just added. |
| relatedno | The older set to which this relationship connection should be made. |
| relationtype | The type of the relationship - duplicate or
altmedia |
| dbhandle | Database handle for the current connection to the database. |
Summary
The linkrelated updates the related
record with the appropriate pointer to the just added record to allow
interlinking of related records. The relationship can be either that
of a duplicate set (relation type: duplicate) that
as come from an alternate vendor or at a different resolution, or an
alternative media (relation type: altmedia) set such as
the video of the same scenario and models as an existing image set.
Name
removedups — remove duplicates from an attribute string
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
scalar removedups( | raw_attribute_list); |
scalar raw_attribute_list;Summary
The removedups function removes any duplicate
entries from a space-separated list of attributes - this is typically
necessary when merging more than one source of attribute information
like that from the kwscore_get function and the
result of fetching model attributes. Please also see removeconflicts
function below.
Name
removeconflicts — remove items that contradict the set attributes from the model attributes
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
scalar removeconflicts( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| model | The model's attributes (mattributes field) |
| existing | The existing combined attributes (ie those taken from the set
scatinfo field |
Summary
The removeconflicts function is designed to stop
contradictory overwriting of mutually exclusive model attributes -
typically those relating to pubic hair trimming, as these can often
vary between sets of the same model. It is provided with the model's
attributes plus the existing set attributes - if the existing set
attributes do not include a contradictory value, then the model's
attributes are included. If there's a conflict, the model's pubic
hair attribute is dropped in favour of that in the set. This is
usually the correct behaviour. This if a model is normally considered
to have a shaven pussy, but appears in a set before she's shaven it
(or even as she does so), then the set may be marked with the hairy
attribute. If that is there, the model's default of shaven will be
removed and only her other attributes (tattoos, piercings, etc) will
be imported.
Name
addassoc — add a new association record connecting a model with a set
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
scalar addassoc( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| setno | the set number to be associated with a model (see below) |
| modelno | the model number to be associated with the above set |
| asstype | the type of the association - currently only G
for general but this might be changed in the future - see the schema
reference for the assoc table for more information.
|
| dbhandle | The open database handle for use in querying the database |
Summary
The addassoc function is designed to add
association records between sets and models. To do this it creates a
new record in the assoc database table using the next
available primary key for that table. To call addassoc
you need to provide a set number, a model number and a dbhandle to a
currently open database session. Optionally you may also provide an
association type although currently only one type, G
for general is defined in the WACS database dictionary. addassoc
protects against adding multiple associations between the same
model and set.
Name
related_set_info — Create a popup menu of possible related sets
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
related_set_info( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| reltype | The type of the relation we're dealing with - rank
or altmedia |
| modelnos | A quoted, comma seperated list of model numbers whose sets should be included in the list. |
| type | The set type of the type we're looking for for rank relations or the type we're NOT looking for for alternative media relations. |
| rank | The type of rank relation we're creating - C for
Continuation records, S for alternative (duplicate)
records |
| setno | The set number we're actually working on (if already known) to be left out of the selection made. |
| default | Allows specification of a set number to be the default - ideal for an update application |
| dbhandle | The handle to the open database connection |
| cgihandle | The handle to the CGI object we're creating a new popup menu using |
| colspan | The colspan attribute to use in the generated table line |
Summary
The related_set_info function outputs a single
line of a table, designed to fit the Standard WACS collection management
tools layout, that adds a pop-up menu using the CGI.pm
library. The purpose of this popup menu is to establish connections between
sets using the saltmedia, snext/sprev
or sduplicates fields.
Name
wacsblogtodb — write a new blog entry into the specified database table
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
scalar wacsblogtodb( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| title | Title of the blog entry (max 80 characters) |
| text | The text for the blog entry (max 4095 characters) |
| table | The database schema to write to - normally the result of doing a
conf_get_attr("table","notes") to get the real name
of the notes schema. This is the default action if this parameter is not
specified. |
| tablekey | Name of the primary key to the table specified above - typically
nentryno for the notes table. This is the default
action if this parameter is not specified. |
| bywhom | Name of the person/entity who made this blog entry. Defaults to
anonymous if not specified. |
| type | Type of blog entry to create - B for standard
Blog, F for Feature article. |
| method | Method of creation - A for Automatic when created
by updatestats or similar, M for
manual when uploading a file using wacsblogctl. |
| dbhandle | The open database handle for use in accessing the database |
Summary
The wacsblogtodb function writes text for a
blog entry into the notes table with the correct formating and splits
it if necessary. At present it will accept blog entries up to 4095 bytes
in length and these can include all of the standard WACS configuration
substitutions (#SITEURL# et al) as handled by
conf_dosubs to allow for icons and set links to be
included quickly and efficiently.
It is provided with the ability to specify the destination table and key in case you wish to use a different database other than notes for the blog. The fields and the structures (with the exception of the primary key) have to be the same, but of course the permissions can be different on that table.
Name
alloc_nextkey — allocate the next new unique primary key for the database table specified
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsStd;
scalar alloc_nextkey( | table_name, | |
| primary_key_fieldname, | ||
dbhandle); |
scalar table_name;scalar primary_key_fieldname;scalar dbhandle;Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| table_name | The name of the table in the Wacs database schema for which the new
key should be allocated, eg sets, models
or assoc. |
| primary_key_fieldname | The name of the primary (unique) key to that database table. |
| dbhandle | The open database handle for use in querying the database |
Table of Contents
![[Warning]](images/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
In Wacs 0.9.2 the exisitng WacsId module was split into two - this part WacsID contains the good routines that are expected to remain as part of the Wacs API in the long term. Those routines that were more questionable and likely to be re-written have been moved to WacsDnl. You need to include both to replicate the pre-0.9.2 functionality |
Table 11.1. Function Summary: Identification Module
| function | description |
|---|---|
| reset_attr | reset the global attribute table |
| id_get_flag | get previously determined flag |
| id_set_attr | store specified attribute for reuse later |
| id_get_info | get previously determined catinfo (ssetflag) |
| id_get_photog | get previously determined photographer |
| id_get_dnldno | get download record number |
| id_get_modelno | get the model number |
| id_get_modelname | get the model's name |
| id_get_vendor | get the vendor reference |
| id_get_dbhandle | get the current DB handle |
| id_get_key | get the current models id at the current vendor |
| id_get_setkey | get the set key at the current vendor |
| id_get_setname | get the name of the most recent set |
| id_get_status | get the status of the most recent set |
| id_get_notes | get the current value of the notes field |
| id_get_setno | get the current value of the setno field |
| id_get_srank | get the current value of the srank field (New in 0.9.0) |
| id_get_sprev | get the current value of the sprev field (New in 0.9.0) |
| id_get_sduplicates | get the current value of the sduplicates field (New in 0.9.0) |
| id_get_saltmedia | get the current value of the saltmedia field (New in 0.9.0) |
| id_get_sdownload | get the current value of the sdownload field (New in 0.9.0) |
| id_get_attr | get the specified attribute for the specified object (New in 0.9.2) |
| media_scan | scan the specified media file for sizes, codecs, etc (New in 0.9.2) |
| media_get_attr | retrieve the requested parameter for the specified media file (New in 0.9.2) |
| media_thumbs | generate appropriate thumbnails for use with video sets (New in 0.9.2) |
| media_settings | provides the current settings for thumbnailing, dimension descriptions, etc (New in 0.9.2) |
| dnld_markdone | mark the download record as successfully done |
| dnld_checkadd | checks or adds a new download record |
| dnld_update | update the download record with new information |
| vend_dnld | return the download location for the specified vendor |
| vid_getsize | get the size of the specified video file |
| find_namestem | look for when known image naming conventions |
| id_gen_proto2struct | process a prototype link url and work out what tokens it contains. |
| id_gen_tokenmatchstring | looks for the specified token |
| id_gen_trymatch | iterates through trying to find matches for the tokens given |
| id_vid_trymatch | special version of id_gen_trymatch which looks only for videos |
| id_gen_findobj | find what the target object is actually called |
| id_gen_getvarval | generalised matching routine used in id_gen_findobj |
| chk_vid_type | check if type extension is a known video file type |
| chkid_existing | see if we already have this idmap for this model/site combination |
The following pages contain the *nix style reference pages for each function call in the WACS ID module. These detail what the function does, what parameters it takes, what it returns and which versions of the WacsId library it is available in. This section is new in WACS 0.9.2 and is incomplete, documenting the most recently added API calls only.
Name
media_scan — Scan the specified media file for attributes
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsId;
scalar media_scan( | pathname); |
scalar pathname;Summary
The media_scan function initiates a scan of the
specified file path for it's detailed attributes. This should include
height and width, codec, etc for all types of media, and additional
information where appropriate like duration for video files. The
initial implementation uses the perl Image::ExifTool library for this
purpose but that may change in time. On completion of the scan, the
filename is returned by the function - this can then be used as the
parameter to media_get_attr to select the specific media object and
attribute to query.
Name
media_get_attr — retrieve the requested parameter for the specified media file
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsId;
scalar media_get_attr( | filename, | |
attribute); |
scalar filename;scalar attribute;Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
height | The height of the video/photo in pixels |
width | The width of the video/photo in pixels |
format | The format of the file: JPEG, PNG, TIFF for images; MOV, MPEG, WMV, for videos |
codec | The Codec format used - Windows Media, MPEG-2, etc |
duration | The running time of a video clip |
creation | The creation date in the corrext format for the current database |
resolution | Text name of the resolution: LD, SD, ID, HD, UHD, Mobile etc |
aspectratio | The actual numeric aspect ratio as a decimal number |
aspect | The generalised aspect ratio expressed as a ratio: 4:3, 16:9, etc |
durhrs | The video clip duration broken up into parts - the hours component |
durmin | The video clip duration - the minutes component |
dursec | The video clip duration - the seconds component |
Summary
The media_get_attr function fetches the
specified result (attribute) of the media file named in the filename
parameter. This is the filename provided by a previously run call
to media scan to perform the actual scan itself. A number of different
media scans can be queried at the same time so long as they do not have
the same file name. The results are all obtained and stored during the
media_scan call and are simply retrieved from a results array when
using media_get_attr.
Name
media_thumbs — generate appropriate thumbnails for use with video sets
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsId;
scalar media_thumbs( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| mode | which mode to work in - usually "icons" or "thumbs" but can be anything - it is appended to the file path |
| start | The number of seconds into the video clip to start producing thumbnails from |
| number | The number of icons/thumbnails to produce for this file |
| step | How many seconds gap there should be between each icon |
| file | The video file to create thumbnails from |
| source | The source directory where the video file can be found |
| dest | The destination directory into where the thumbnails should be written |
| stem | Provides an alternative filename stem for the output thumbnail |
Name
media_settings — provides the current settings for thumbnailing, dimension descriptions, etc
Synopsis
use Wacs;
use Wacs::WacsId;
scalar media_settings( | ...); |
Parameters
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
filename | Name of the XML file to parse for settings info (Not active yet) |
Summary
The media_settings returns a data structure
containing the configuration parameters for various media operations.
The object thumbs within this data structure contains
an array of settings for thumbnails for a given duration of video clip.
This contains min and max which
determines the minimum and maximum number of seconds duration that this
rule applies to. There is also desc which describes
the rule and number which tells you how many thumbnail
locations will be produced by the rule. There is then a pos
object which describes what each location is, providing start
and tail for each cluster of auto generated thumb nails.
The value for start is between 0 and 1 and indicates where
the thumbnail should be taken from - for instance 0.33
indicates this thumbnail should be taken 33% of the way through the video
clip.
Table of Contents
![[Warning]](images/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
In Wacs 0.9.2 the exisitng WacsId module was split into two - this part WacsDnl contains the bad routines that are expected to be re-written and not to remain part of the Wacs API in the long term. Those routines that were more stable and likely to remain have been moved to WacsId. You need to include both modules to replicate the pre-0.9.2 functionality |
Table 12.1. Function Summary: Downloading Module
| function | description |
|---|---|
| ident_img | Identify characteristics of an image set from download info |
| ident_vid | Identify characteristics of a video clip from download info |
| dnld_img | retrieve a download record based upon the namestem |
| id_mpage | process a modelpage looking for links to suitable sets |
| id_i_fetch | |
| find_cookies | |
| extractphotog |
This is the Database Schema Reference Manual, or data dictionary, for the WACS environment. This documents the database tables in use, their contents, structure, relationships and assigned values.
The WACS database schemas are built with the convention that the
first letter of the schema name is prefixed to all fields within that
schema. Thus a field from the sets schema will start with the letter
s, a field from the assoc schema will start with
the letter a and so on. Generally relationed fields
will have fundamentally the same name, such that the set number is
setno in the sets schema, asetno in the
assoc schema, tsetno in the tags schema,
dsetno in the download schema, and so on.
This makes performing relational
joins much easier and more portable since one can do the likes of
where amodelno = modelno without any ambiguity and
without having to specify the table name explicity.
Where possible fields with a limited set of possible values will be
single character fields with a reasonably neumonic value for each
possible value. Thus the media type (stype, dtype, etc) is
V for Video Clip, I for Image Set,
D for DVD scene, and so on. A lookup hash of the legal
values will typically be available for programmers to use from the core Wacs
module (see the Part II, “WACS API Programming Reference” for more details).
Chapter 13, Schema Reference: Sets
Chapter 14, Schema Reference: Assoc
Chapter 15, Schema Reference: Idmap
Chapter 16, Schema Reference: Models
Chapter 17, Schema Reference: Download
Chapter 18, Schema Reference: Photographer
Chapter 19, Schema Reference: Tag
Chapter 20, Schema Reference: Vendor
Chapter 21, Schema Reference: Conn
Chapter 22, Schema Reference: Keyword
Chapter 23, Schema Reference: Wacsuser
Chapter 24, Schema Reference: Attrib
Chapter 25, Schema Reference: Notes
Table of Contents
- 13. Schema Reference: Sets
- 14. Schema Reference: Assoc
- 15. Schema Reference: Idmap
- 16. Schema Reference: Models
- 17. Schema Reference: Download
- 18. Schema Reference: Photographer
- 19. Schema Reference: Tag
- 20. Schema Reference: Vendor
- 21. Schema Reference: Conn
- 22. Schema Reference: Keyword
- 23. Schema Reference: Wacsuser
- 24. Schema Reference: Attrib
- 25. Schema Reference: Notes
Table of Contents
![[Warning]](images/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
WACS 0.8.5 contains a significant number of additions to this schema ahead of the shift to the 0.9.x release series. None of these changes are used or accessed by applications in Wacs 0.8.5, so you can defer updating the Schema until Wacs 0.9.0 comes out if you wish to. There will be a tool to update the schema supplied with Wacs 0.9.0; this appeared in the wacs 0.8.6 release and is called wacsschema. It is integrated into the existing wacssetup tool which can now perform upgrades as well as first time initialisation. The newly added and currently not used fields are those in bold typeface. |
create table sets ( setno number(9) primary key, stype char(1) not null, sstatus char(1) not null, srank char(1), sauto char(1), srating char(1), sflag char(1), stechqual number(2), svariety number(2), svisits number(2), sformat varchar2(10), scodec varchar2(40), stitle varchar2(240), sofftitle varchar2(240), sofficon varchar2(160), saddicon varchar2(160), sname varchar2(80), shair varchar2(80), smodelno varchar2(40), slocation varchar2(20), slocdetail varchar2(40), sattire varchar2(20), sfocus char(1), sphotog varchar2(6) references photographer, ssource varchar2(80), sfoundry varchar2(80), sproddate date, sreldate date, suscattr char(1), snotes varchar2(240), sdesc varchar2(2048), sindexes number(6), simages number(6), sdurhrs number(2), sdurmin number(2), sdursec number(2), slandx number(6), slandy number(6), sportx number(6), sporty number(6), saspect varchar2(10), sfps number(6), sinter char(1), sskipfr number(9), sbytes number(12), sdvdno number(6), sdvddisc number(2), sdvdtitle number(3), sdvdstartch number(3), sdvdendch number(3), sidlogo char(1), serrors char(1), sduplicates number(9) references sets, saltmedia number(9) references sets, snext number(9) references sets, sprev number(9) references sets, ssetpos number(2), scatinfo varchar2(160), scatflag char(1), snamestem varchar2(80), sdownload varchar2(160), sarea varchar2(160), scategory varchar2(160), sdirectory varchar2(240), scomments varchar2(240), sadded date, samended date );
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
|
![[Tip]](images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
The new fields introduced in WACS 0.8.5 are |
Table 13.2. sstatus: Status of Set: defined values
| sstatus | |
|---|---|
| M | Manually Added, Details Not Checked |
| A | Automatically Added, Details Not Checked |
| N | Normal - Checked |
| G | Good - Thoroughly Checked |
| U | Unknown |
Table 13.3. sauto: Automatic Update of Set Allowed?: defined values
| sauto | |
|---|---|
| N | None (no auto updates) |
| L | (on-disk) Location only - all attributes manual |
| A | Append only - all existing entries stay |
| F | Fully auto-generated - all values can change |
Table 13.4. srating: Overall Rating For The Set: defined values
| srating | |
|---|---|
| 5 | Finest |
| 4 | Very Good |
| 3 | Good |
| 2 | Reasonable |
| 1 | Mediocre |
| 0 | None Specified |
Table 13.5. stechqual: Technical Quality Rating For The Set: defined values
| stechqual | |
|---|---|
| 5 | Finest - HD Video done well, Multi-megapixel stills |
| 4 | Very Good - Well lit SD or good HD Video, good megapixel + stills |
| 3 | Good - Well done low-res SD, good sub-megapixel stills; not quite so good but higher res |
| 2 | Reasonable - either very small, or bad equipment (flash on camera) used moderately well |
| 1 | Mediocre - lack of skill, bad equipment, poor composition |
| 0 | None Specified |
Table 13.6. svariety: Unusualness Rating For The Set: defined values
| svariety | |
|---|---|
| 5 | Very Unusual - look at the set scenario and think "What the F***!" |
| 4 | Unusual - unusual and very interesting - "Wow" |
| 3 | Neat - interesting and impressive but not quite "Wow" |
| 2 | Cute Twist - a slightly unusual twist, unusual pose etc |
| 1 | Ordinary - can still score very highly in overall and tech |
| 0 | None Specified |
Table 13.7. sformat: Format of the File(s) In The Set: defined values
| sformat | |
|---|---|
| JPEG | JPEG image |
| GIF | GIF image |
| PNG | PNG image |
| PNM | PNM,PBM,PGM,PPM image |
| WMV | Windows Media Player Video |
| AVI | AVI Video (codec specified separately) |
| QT | QuickTime .mov Video (codec specified separately) |
| MPEG | MPEG Video (MPEG-1 or 2) |
Table 13.8. sidlogo: Presence of Burnt-in Logo: defined values
| sidlogo | |
|---|---|
| U | Unknown |
| Y | Yes - image/video has burnt-in logo |
| N | No - image/video is clean of bugs |
Table 13.9. sinter: Progressive or Interlaced Video Structure
| sinter | |
|---|---|
| I | Video has interlaced frame/field structure |
| P | Video has progressive frames (atomic) |
Table 13.10. serrors: Presence of Known Errors: defined values
| serrors | |
|---|---|
| N | None detected |
| F | Fixed - faulty images/video have been fixed - Quality may have been compromised - sizes/signatures no indicative of original |
| E | Encoding Only - causes message but renders OK |
| C | Some Corrupt Images/Segments of video |
Table 13.11. scatflag: Generalised type of the set: defined values
| scatflag | |
|---|---|
| F | Fuck - straight sex |
| L | Lesbian - lesbian sex |
| G | Group - more than two people having sex, mixed-gender |
| T | Toy - Solo but uses toys such as dildo, vibrator, etc |
| S | Solo - Model on her own (possibly with a non-participatory audience) |
| M | Masturbation - Solo but includes masturbation activities |
| N | None - not determined yet |
| B | Backstage - Behind The Scenes set featuring this model |
| C | Clothed - non-nude set featuring this model |
| D | Duplicate - duplicate set - maybe from a different site - DEPRICATED |
Table 13.12. srank: role and position of set: defined values
| srank (defined values) | |
|---|---|
| P | Primary (Main) - a standard freestanding record |
| C | Continuation - a subsequent part of a set split over mulitple sets, most often a movie clip |
| S | Secondary (Alternate) - an alternative version of another set - a different resolution, a split media file, or the same set as distributed by another vendor. |
Table 13.13. slocation: generalised description of locations: recommended values
| slocation (recommended values) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Balcony | Balcony or Terrace; outdoors but not part of Garden | |||
| Bathroom | Bathroom, Toilet or Shower Cubicle | |||
| Bedroom | Bedroom or other sleeping area | |||
| Country | Country - including Beach, Forest, and Fields | |||
| Dining Room | Dining Room or Eating Area | |||
| Garden | Garden or other private outdoor area | |||
| Hallway | Hallway, Staircase or Entrance | |||
| Kitchen | Kitchen or Kitchen area of apartment | |||
| Laundry | Laundry, Cleaning or Utility Area | |||
| Lounge | Lounge, Sitting Room or Other Seating Area | |||
| Office | Office, including Home PC desk | |||
| Other Room | Any other room - (Domestic) Library, Junk Room, Garage, etc | |||
| Specialised | Specialised Location: Swimming Pool, Shop, Recording or TV Studio, Factory, Railway Station, etc; additional details can be placed in slocdetail. | |||
| Sports | Location associated with Sports and Exercise: Gym, Locker Room, etc. | |||
| Studio | White or other plain background Photographic Studio - but NOT Television or Audio recording studios as a feature of the set theme | |||
Table 13.14. sattire: generalised description of model's clothing: recommended values
| sattire (recommended values) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Business | A tidy business suit or other combination appropriate to an office environment. | |||
| Casual | A pretty general category - jeans, denim skirts, summer dresses | |||
| Elegant | Particularly stunning dresses or formal evening wear. | |||
| Fantasy | Fantasy costumes of all sorts. | |||
| Glamourous | A glamourous party dress or similar that is quite risque and is likely to spontaneously reveal the woman's assets! | |||
| Housewear | The sort of clothing that is worn casually about the house but not normally in public. | |||
| Hospitality | Housemaids and Waitress Uniforms | |||
| Law Enforcement | Police and Security Guard Uniforms | |||
| Medical | Uniforms appropriate to the Medical Industry | |||
| Military | Uniforms appropriate to the Military Services | |||
| Nightwear | Pajamas, Baby Doll dresses, Nightshirts | |||
| Nothing | Nude! | |||
| Partial | Only partially clothed | |||
| Retail | Uniforms appropriate to the Retail and other service industries (but not Maids) | |||
| Schoolwear | Various uniforms associated with Schoolgirls including cheerleaders and gym slips | |||
| Smart | Smart or attractive clothes suitable for going to a party without being elegant or stunning. | |||
| Sports | Sportswear - track suits, sports bras, cycling outfit, etc | |||
| Swimwear | Bikinis and other swimming costumes | |||
| Underwear | Just a bra and panties, or similar - BUT does not include a tank top plus panties which with the addition of a skirt or jeans would be presentable outdoor wear. | |||
Table 13.15. suscattr: how to generate the 18 USC 2257 declaration: defined values
| suscattr | |
|---|---|
| V | Vendor based - use vendor's USC declaration address |
| E | Exempt - for pure nude sites without sexual activity of any kind |
| P | Photographer based - use photographer's address for USC declaration |
| N | Suppress declaration - NOT RECOMMENDED FOR US RESIDENTS |
| G | Generic - include generic text with all vendor addresses |
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
A possible future direction is for this table to be
relationally linked to the vendors table such that
|
create table idmap ( identryno number(7) primary key, imodelno number(6) references models, istatus char(1), isite varchar2(20) not null, ikey varchar2(30), ialtkey varchar2(30), iname varchar2(30), inotes varchar2(80), iactive char(1), ichanged date, ichecked date, iadded date, iamended date );
Table 15.1. istatus: idmap status: defined values
| istatus | |
|---|---|
| M | Manually Added |
| A | Generated Automatically |
| I | Imported From Another WACS site |
Table 15.2. iactive: model activity status as this identity: defined values
| iactive | |
|---|---|
| Y | Yes - active model (refresh list with auto tools) |
| D | Dormant - no new sets for a while (don't bother checking) |
| N | No - inactive (id not known) |
| O | Obsolete - old reference (no longer there) |
Table 15.3. isite: Some recommended site abbrievations: recommended values
| isite (recommended values) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| 21SEX | 21sextury.com | |||
| ALS | ALSScan.com | |||
| AMK | AMKingdom.com (aka ATK Galeria) | |||
| ATE | ATKExotics.com | |||
| ATKP | ATKPremium.com | |||
| AW | AbbyWinters.com | |||
| C17 | ClubSeventeen.com | |||
| DDF | ddfprod.com | |||
| FJ | FemJoy.com | |||
| IFG | infocusgirls.com | |||
| JAFN | jennyandfriends.net | |||
| KPC | karupspc.com (aka Karup's Private Collection) | |||
| KHA | karupsha.com (aka Karup's Hometown Amateurs) | |||
| SE | sapphicerotica.com | |||
| TF | teenflood.com | |||
| PMET | PinkMetallic.com, the WACS Demo site | |||
Table of Contents
![[Warning]](images/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
WACS 0.8.5 contains a significant number of additions to this schema ahead of the shift to the 0.9.x release series. None of these changes are used or accessed by applications in Wacs 0.8.5, so you can defer updating the Schema until Wacs 0.9.0 comes out if you wish to. There will be a tool to update the schema supplied with Wacs 0.9.0. The newly added and currently not used fields are those in bold typeface. |
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Please notice that the use of metric in the vital statistics is not intended to be a dig at the imperial measurements, merely that it reliably and consistantly conveys the necessary information as sensible, manageable integers. Utility functions are planned to make it easier to convert and update in a future release of WACS. You try writing an SQL query to find models between 5ft 3ins and 5ft 6ins in height, as compared to between 160 and 168 cms in height. See what I mean? |
create table models ( modelno number(6) primary key, mname varchar2(40), mhair varchar2(15), mlength varchar2(20), mtitsize varchar2(10), mcupsize char(1), meyes varchar2(15), mrace varchar2(15), mattributes varchar2(60), maliases varchar2(60), mdisting varchar2(80), musual varchar2(60), mimage varchar2(80), mbigimage varchar2(80), mbodyimage varchar2(80), maltimage varchar2(80), mstatus char(1), mrating char(1), mpussy char(1), mlabia varchar2(80), mflag char(1), mvideos char(1), msolo char(1), mstraight char(1), mlesbian char(1), mfetish char(1), mmast char(1), mtoys char(1), mother char(1), mnsets number(4), mnimages number(7), mnvideos number(4), mcountry varchar2(30), mhometown varchar2(80), mage number(3), mageyear number(4), mcstatus char(1), mvitbust number(4), mvitwaist number(4), mvithips number(4), mbuild char(1), mheight number(3), mweight number(3), mdress number(2), mstarsign number(2), moccupation varchar2(30), mcontact varchar2(80), mbirthdate date, monfile char(1), magency varchar2(80), mnotes varchar2(240), mbio varchar2(240), madded date, mamended date );
Table 16.1. mstatus: model record status: defined values
| mstatus | |
|---|---|
| A | Automatically Added, Details Not Checked |
| M | Manually Added, Details Not Checked |
| N | Normal - Checked |
| G | Good - Thoroughly Checked |
| P | Placeholder - Not Real Person |
Table 16.2. mrating: model rating: defined values
| mrating | |
|---|---|
| 5 | Finest (included in Q= searches and front page) |
| 4 | Very Good (included in Q= searches and front page) |
| 3 | Good (not included in Q= searches, included in front page) |
| 2 | Reasonable (not included in Q= searches or front page) |
| 1 | Mediocre (not included in Q= searches or front page) |
| 0 | None Specified (listed in U= searches) |
Table 16.3. mpussy: model's normal pubic hair style: defined values
| mpussy | |
|---|---|
| H | Hairy |
| T | Trimmed |
| B | Brazilian style shaved - very little hair above clit area |
| S | Shaven - completely |
| V | Varies (best avoided, try and pick one of above - her usual style) |
| N | Not Specified |
Table 16.4. mflag: special marking flag for models: defined values
| mflag | |
|---|---|
| S | Favourite Solo |
| L | Favourite Lesbian |
| C | Favourite Cutie |
| F | Favourite Straight |
| M | Current Featured Model |
| P | Placeholder (not a real person) |
Table 16.5. model activites flags: defined values
| model activities flags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fieldname | possible values | |||
| ||||
| mvideos | Y - Yes, does this; N - No, doesn't do this | |||
| msolo | ||||
| mstraight | ||||
| mlesbian | ||||
| mfetish | ||||
| mmast | ||||
| mtoys | ||||
| mother | ||||
Table 16.6. mcstatus: accuracy of home country field: defined values
| mcstatus | |
|---|---|
| C | Certain - country of origin stated in bio |
| Q | Quasi-authoritative - from third party site |
| I | Inferred - from location or other models seen with |
| G | Guess - based on photographer or building style |
| N | None |
Table 16.7. mrace: race of the model: defined values
| mrace | |
|---|---|
| Caucasian | Caucasian - European Descent aka White |
| Oriental | Oriental - Chinese, Japanese, SE Asian |
| Asian | Indian Sub-Continent - India, Pakistan, etc |
| Negroid | Negroid - of African Descent aka Black |
| Aboriginal | Aboriginal - indigenous peoples - First Nation, Polynesian, etc |
| Latina | Latin American - aka Hispanic |
| Mixed | Mixed race and others |
Table 16.9. mlabia: about the model's labia: defined values
| mlabia | |
|---|---|
| I | Internal (No Projection) |
| C | Cameltoe |
| T | Thin Projection |
| B | Broad Projection |
Table 16.10. mstarsign: The models astrological star sign
| mstarsign | |
|---|---|
| null or '' | Unknown |
| Aries | Aries (21 Mar) |
| Taurus | Taurus (21 Apr) |
| Gemini | Gemini (21 May) |
| Cancer | Cancer (21 June) |
| Leo | Leo (22 Jul) |
| Virgo | Virgo (23 Aug) |
| Libra | Libra (23 Sep) |
| Scorpio | Scorpio (23 Oct) |
| Sagittarius | Sagittarius (22 Nov) |
| Capricorn | Carpicorn (22 Dec) |
| Aquarius | Aquarius (21 Jan) |
| Pisces | Pisces (20 Feb) |
Table 16.11. vital statistics: meanings
| vital statistics | |
|---|---|
| mweight | Weight in Kilos |
| mheight | Height in centimetres |
| mvitbust | Bust measurement in centimetres (vital stats part 1) |
| mvitwaist | Waist measurement in centimetres (vital stats part 2) |
| mvithips | Hips measurement in centimetres (vital stats part 3) |
| mdress | Dress size given in European standard sizes |
Table of Contents
create table download ( downloadno number(7) primary key, dmodelno number(6) references models, dsetno number(9) references sets, dstatus char(1), dtype char(1), dsite varchar2(20) not null, dkey varchar2(30), dsetkey varchar2(40), dsetname varchar2(240), dsetflag char(1), dnotes varchar2(240), durl varchar2(240), darchive varchar2(240), dsignature varchar2(82), dsize number(12), dproddate date, dreldate date, dphotog varchar2(6) references photographer, dbranding varchar2(20), dpulled date, dadded date, damended date );
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The dsize field was expanded from 9 digits to 12 digits in Wacs 0.9.2 to allow for video files larger than 1GB to be correctly described. |
Table 17.1. dstatus: download status: defined values
| dstatus | |
|---|---|
| U | Not Yet Attempted |
| F | Failed - Retry when possible |
| S | Successful - set registered in database, available |
| P | Pending - downloaded, awaiting unpacking |
| A | Aborted - don't download for some reason |
| D | Deferred - held back from being downloaded |
| R | Relationship Entry - a second model for a set |
| L | Liasion - a proto-Relationship Entry not yet linked |
| E | Error - not the right model, etc |
| I | In Progress - download currently in progress |
| X | Incomplete - record of it's existance but too little info to download it |
Table 17.3. dsetflag: Suggested value for scatflag based on parsing result
| dsetflag | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Table of Contents
create table photographer ( pref varchar2(6) primary key, pname varchar2(40), paliases varchar2(80), pgender char(1), paddress varchar2(120), pemail varchar2(80), pwebsite varchar2(80), pusual varchar2(40), pregion varchar2(20), pcountry varchar2(50), plocation varchar2(50), pstyledesc varchar2(80), prating number(2), phardness number(2), psolo char(1), ptoys char(1), plesbian char(1), pstraight char(1), pgroup char(1), pfetish char(1), pdigital char(1), pfilm char(1), pvideo char(1), phdvideo char(1), pcamera varchar2(40), pcamnotes varchar2(80), pcomments varchar2(240), pnotes varchar2(240), pbiography varchar2(1024), padded date, pamended date );
Table 18.2. pregion: geographical location of the photographer: defined values
| pregion | |
|---|---|
| Europe | Europe |
| North America | USA and Canada |
| South America | South and Central America |
| Middle East | Middle East (brave photographer!) |
| Asia | Asia (India and the Indian Sub-continent ONLY) |
| Orient | Orient (Asia excluding Indian Sub-continent) |
| Australasia | Australia and New Zealand |
| Africa | Africa |
| Other | Other |
Table 18.3. prating: overall rating of photographer: defined values
| prating | |
|---|---|
| 0 | None |
| 1 | Awful - poor equipment and technique |
| 2 | Poor - uninteresting and badly composed/exposed work |
| 3 | Reasonable - technically OK, but very unenterprising |
| 4 | Good - good technique, interesting compositions and direction |
| 5 | Excellent - Excellent technique, interesting and challenging compositions and direction |
Table 18.4. phardness: rating of how explicit this photographer can be: defined values
| phardness | |
|---|---|
| 0 | None - Not Rated |
| 1 | Soft-focus (very arty) |
| 2 | Glamour - sharp but no open leg, genital detail, etc |
| 3 | Normal - wide range of shots but not particularly strong |
| 4 | Hard (close-ups) |
| 5 | Fetish - pretty extreme, gaping, etc |
Table 18.5. photographer activites covered flags: defined values
| photographer activities covered flags | |
|---|---|
| fieldname | possible values |
| psolo | Y - Yes, does this; N - No, doesn't do this; O - Occasionally does this |
| ptoys | |
| plesbian | |
| pstraight | |
| pgroup | |
| pfetish | |
Table 18.6. photographer technologies used flags: defined values
| photographer technologies used flags | |
|---|---|
| fieldname | possible values |
| pdigital | Y - Yes, uses this technology; N - No, doesn't use this technology. |
| pfilm | |
| pvideo | |
| phdvideo | |
Table of Contents
create table tag ( tagno number(9) primary key, tmodelno number(6) references models, tsetno number(9) references sets, tstatus char(1), tflag char(1), tgroup number(6), tdesc varchar2(40), towner varchar2(20), texpiry date, tadded date, tamended date );
Table 19.1. tstatus: tag entry status: defined values
| tstatus | |
|---|---|
| T | Temporary - expire as per expiry rules |
| V | Viewed, Temporary - expire as per expiry rules, hide from index |
| P | Permanent - don't expire, show in index |
| A | Archived - don't expire, don't show in normal indexes |
Table 19.2. tflag: tag content type status: defined values
| tflag | |
|---|---|
| M | Model-based tag entry |
| S | Set-based tag entry |
Table of Contents
create table vendor ( vsite varchar2(20) primary key, vname varchar2(45), vshortname varchar2(20) not null, vregion varchar2(20), vcountry varchar2(50), vweburl varchar2(120), vsignup varchar2(120), vrating number(2), vtechrate number(2), vuscdecl varchar2(240), vcurrent char(1), vshow char(1), vsubscribed char(1), vuntil date, vusername varchar2(80), vpassword varchar2(30), vidtimg number(2), vidtvid number(2), vcomexcl varchar2(240), vmdirectory varchar2(240), vmdiruse char(1), vmdirpages number(3), vmpage varchar2(240), vmpaguse char(1), vmbio varchar2(240), vmbiouse char(1), vmvideos varchar2(240), vmviduse char(1), vvidpage varchar2(240), vviduse char(1), vimgpage varchar2(240), vimguse char(1), valtpage varchar2(240), valtuse char(1), vsrvimg varchar2(240), vsrvvid varchar2(240), vmultimg char(1), vmultvid char(1), vnotes varchar2(240), vadded date, vamended date );
Table 20.1. vcurrent: vendor existance status: defined values
| vcurrent | |
|---|---|
| Y | Yes - still an active site |
| N | No - no longer trading at that web address |
Table 20.2. vshow: vendor index inclusion status: defined values
| vshow | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| Y | Yes - show in indices | |||
| N | No - hide from indices | |||
Table 20.3. vmdiruse et al: vendor URL auto-usuability status: defined values
| vmdiruse et al | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| fieldname | page purpose | possible values | |
| vmdiruse | Model Directory | Y | link is (auto)usable |
| vmpaguse | Model Page | N | link is not (auto)usable |
| vmbiouse | Model Biography | S | link usable only with session key |
| vmviduse | Model's Videos Page | ||
| vviduse | Video Set Page | ||
| vimguse | Image Set Page | ||
| valtuse | Alternate Image Set Page | ||
Table of Contents
create table conn ( centryno number(9) primary key, cgroup number(6), corder number(3), cflag char(1), cstatus char(1), cmodelno number(6) references models, csetno number(9) references sets, cphotog varchar2(6) references photographer, ctype varchar2(20) not null, cdesc varchar2(80), ccomments varchar2(240), cpath varchar2(160) cadded date, camended date );
![[Warning]](images/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
Conn (connections) is a recent addition and not all parts of the toolchain are in place yet. As the management tools are added, it is expected that at least the legal values for fields will change and be expanded. |
Table 21.1. cflag: connection type: defined values
| cflag | |
|---|---|
| A | Ad-Hoc - A casual index of some random theme |
| G | Gallery - A slightly more focused collection with a specific concept behind it. |
Table 21.2. cstatus: connection entry status: defined values
| cstatus | |
|---|---|
| M | Manually Added |
| T | Imported from a Tag set |
Table of Contents
create table keyword ( kentryno number(9) primary key, kflag char(1), kword varchar(30) not null, kexclusions varchar(120), kiloc varchar(20), kiscore number(1), kicat char(1), kicscore number(1), kidet varchar(40), kidscore number(1), kiattr varchar(30), kiascore number(1), kiwear varchar(40), kiwscore number(1), kiother varchar(40), kioscore number(1), knotes varchar(80), kadded date, kamended date );
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
From WACS 0.8.2, the kiother and kioscore fields are used to determine values for the sattire field in the sets schema. New fields kiwear and kiwscore were introduced in WACS 0.8.5 and will be used for values for the sattire fields from WACS 0.9.x freeing kiother and kioscore for their original purpose of being spare for future functionality. |
Table of Contents
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
This schema has been renamed wacsuser as on certain DBs (eg Oracle) user is a reserved word. |
create table wacsuser ( userid number(9) primary key, username varchar2(20) not null, upassword varchar2(20) not null, ustatus char(1), utype char(1), uvisits number(6), uclass varchar2(20) not null, uprexcl varchar2(20), uprdirect char(1), uprpage varchar2(20), uprscale varchar2(20), uprsize varchar2(12), uprquality number(3), uprdelay number(3), uprunits char(1), uprthumbs varchar2(20), uprother varchar2(20), uregister date, uexpiry date, ulastact date, ulastconn date, ulastcomm date, ulasttopic varchar2(40), upurge date, uemail varchar2(120), ualtemail varchar2(120), uscreenname varchar2(30), urealname varchar2(80), uaddress1 varchar2(80), uaddress2 varchar2(80), ucity varchar2(50), uprovince varchar2(30), ucountry varchar2(30), upostcode varchar2(20), utelephone varchar2(30), uallowed char(1), uthirdp char(1), ujointhru varchar2(30), ureference varchar2(120), upayamount number(4,2), upaycurr varchar2(10), ulinkfrom varchar2(120), urebill char(1), ucommpay char(1), ucommission varchar2(80), ucommfee number(4,2), ucommcurr varchar2(10), ucommperc number(3), unotes varchar2(240), uadded date, uamended date );
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The |
Table 23.1. ustatus: User Account Status: defined values
| ustatus | |
|---|---|
| A | Active - this account is currently active |
| E | Expired - this user account has expired |
| P | Pending - user needs to complete verification step |
| S | Suspended - access temporarily suspended - leaked password, etc |
Table 23.2. utype: User Type: defined values
| utype | |
|---|---|
| A | Administrator - account used for system management |
| F | Friend (or Freebie) - account granted free access |
| S | Subscriber - a subscription account |
Table 23.3. uclass: User Class: defined values
| uclass | |
|---|---|
| viewer | a normal user account |
| power | power user with enhanced rights, can see most of the administration tools but can't make significant changes to the collection. Primarily intended for support staff |
| admin | system and collection administrator - full administrative rights |
Table of Contents
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The attrib schema was introduced in WACS 0.8.5 but is not used at all by that release. It is used in Wacs 0.8.6 and higher. |
create table attrib ( atrecno number(9) primary key, atkeyword varchar2(30), atsource char(1), atrecognise char(1), atallowadd char(1), atdisplay char(1), atshortdesc varchar2(50), atlongdesc varchar2(240), aticon varchar2(160), atgroup varchar2(30), atimplicit char(1), atvalidset char(1), atvalidmodel char(1), atvalidother char(1), atmarkset char(1), atmarkmodel char(1), atmarkother char(1), atsetsearch char(1), atmodsearch char(1), atcombsearch char(1), atothsearch char(1), atsetdetail char(1), atmoddetail char(1), atcombdetail char(1), atothdetail char(1), atnotes varchar2(240), atadded date, atamended date );
The atrecno is a sequentially incremented reference
number. Standard attributes typically will be numbered between 1 and 99,
extended attributes between 100 and 499. Custom attributes should be given
a number from 500 upwards to avoid clashes with attributes added to future
WACS distributions.
Table 24.1. atsource: attribute source: defined values
| atsource | |
|---|---|
S | Standard - normal wacs attributes |
E | Extended - more unusual wacs attributes |
C | Custom - locally added attribute |
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
For more information on these attributes and their meanings, please see the explanation in the Customisation chapter of the administration guide. |
Table of Contents
create table notes ( nentryno number(9) primary key, ntype char(1), norder number(3), ntitle varchar2(80), ntext varchar2(2048), nstatus char(1), nnext number(9) references notes, nexpiry date, nmodelno number(6) references models, nsetno number(9) references sets, nphotog varchar2(6) references photographers, nconn number(6), ncomments varchar2(120), nadded date, namended date );
![[Warning]](images/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
Notes is a brand new addition as at Wacs 0.8.5 and is not going to be used until at least the next release of Wacs. It is intended to provide a mechanism for attaching additional text to models, connections and as a basis for a simple site blog mechanism. All values given below are subject to change therefore. |
Table 25.1. ntype: notes type: defined values
| ntype | |
|---|---|
| B | Site Blog entry |
| C | Connection Descriptive Text - more about a connection |
| M | Model Biography - an extended biography |
A
- addassoc, Standard Components Module: Reference
- addconticons, User Interface Module: Reference
- addheadercss, Core Module: Reference
- addkeyicons, User Interface Module: Reference
- Using ..., Introducing WacsUI
- addlinks, User Interface Module: Reference
- addratings, User Interface Module: Reference
- addrelicons, User Interface Module: Reference
- add_auth, Core Module: Reference
- alloc_nextkey, Standard Components Module: Reference
- alsofeaturing, User Interface Module: Reference
- assoc
- astatus values, Assoc: Defined Values
- Field Listing, Assoc: Schema SQL
- making connections, Connecting Sets And Models
- astatus, Assoc: Defined Values
- attrib
- Field Listing, Attrib: Schema SQL
- auth_error, Core Module: Reference
- auth_get_attr, Core Module: Reference
- auth_user, Core Module: Reference
- Automatic Thumbnails
- Size, count and position settings (media_settings), Identification Module: Reference
C
- cacheloc, Core Module: Reference
- callframe, Standard Components Module: Reference
- cflag, Conn: Defined Values
- checkexclude, Core Module: Reference
- checkindex, Core Module: Reference
- check_auth, Core Module: Reference
- Configuration
- Reading The..., A First WACS Program
- Configuration Values
- Getting..., Initialising Database Connection
- conf_dosubs, Core Module: Reference
- conf_get_attr, Initialising Database Connection, Core Module: Reference
- conn
- cflag values, Conn: Defined Values
- cstatus values, Conn: Defined Values
- Field Listing, Conn: Schema SQL
- Connection
- Database, Initialising..., A First WACS Program
- contentlink, User Interface Module: Reference
- Using...., Using the contentlink function
- cstatus, Conn: Defined Values
D
- Data Architecture, Connecting Sets And Models
- Database
- Environment Variables, Initialising Database Connection
- Fetching Records..., A First WACS Program
- Initialising Connection To..., A First WACS Program
- dberror, Core Module: Reference
- describeher, User Interface Module: Reference
- WacsUI: Introducing, Introducing WacsUI
- divideup, Core Module: Reference
- download
- dsetflag values, Download: Defined Values
- dstatus values, Download: Defined Values
- dtype values, Download: Defined Values
- Field Listing, Download: Schema SQL
- dsetflag, Download: Defined Values
- dstatus, Download: Defined Values
- dtype, Download: Defined Values
- Dynamic Content, WACS and Web 2.0
F
- findmodel, Standard Components Module: Reference
- findrecentmodels, Standard Components Module: Reference
- findrecentsets, Standard Components Module: Reference
- find_config_location, Core Module: Reference
- foundatsite, Standard Components Module: Reference
G
- getcontinfo, Standard Components Module: Reference
- getgallery, Standard Components Module: Reference
- geticonlist, Core Module: Reference
- getrelated, User Interface Module: Reference
- gettoday, Core Module: Reference
- gettypecolour, Core Module: Reference
- getvaluename, Core Module: Reference
- getvideoext, User Interface Module: Reference
I
- iactive, Idmap: Defined Values
- iconlink, User Interface Module: Reference
- Using ...., iconlink: WacsUI's Most Important Function
- icons
- adding set ..., About Set Display
- idmap
- Field Listing, Idmap: Schema SQL
- iactive values, Idmap: Defined Values
- isite recommended values, Idmap: Defined Values
- istatus values, Idmap: Defined Values
- isite, Idmap: Defined Values
- istatus, Idmap: Defined Values
K
- keyword
- Field Listing, Keyword: Schema SQL
- kflag values, Keyword: Defined Values
- kflag, Keyword: Defined Values
- kwscore_get, Standard Components Module: Reference
- kwscore_process, Standard Components Module: Reference
- kwscore_reset, Standard Components Module: Reference
L
- linkfromprevious, Standard Components Module: Reference
- linkrelated, Standard Components Module: Reference
- loadattrvalues, Core Module: Reference
M
- makedbsafe, Core Module: Reference
- masthead, Standard Components Module: Reference
- mbuild, Models: Defined Values
- mcstatus, Models: Defined Values
- media_get_attr, Identification Module: Reference
- media_scan, Identification Module: Reference
- media_settings, Identification Module: Reference
- media_thumbs, Identification Module: Reference
- menu_get_body, User Interface Module: Reference
- menu_get_default, User Interface Module: Reference
- menu_get_entry, User Interface Module: Reference
- menu_get_handler, User Interface Module: Reference
- menu_get_title, User Interface Module: Reference
- mfetish, Models: Defined Values
- mflag, Models: Defined Values
- mheight, Models: Defined Values
- mlabia, Models: Defined Values
- mlesbian, Models: Defined Values
- mmast, Models: Defined Values
- modelheads, Standard Components Module: Reference
- modelheadshot, Standard Components Module: Reference
- modelmast, Standard Components Module: Reference
- models
- activities values, Models: Defined Values
- connection to sets, Connecting Sets And Models
- Field Listing, Models: Schema SQL
- hiding unwanted ones, Avoiding Placeholder Models
- mbuild values, Models: Defined Values
- mcstatus values, Models: Defined Values
- mflag values, Models: Defined Values
- mlabia values, Models: Defined Values
- mpussy values, Models: Defined Values
- mrace values, Models: Defined Values
- mrating values, Models: Defined Values
- mstarsign values, Models: Defined Values
- mstatus values, Models: Defined Values
- vital statistics fields, Models: Defined Values
- modelsel.php, WACS and Web 2.0
- Modules
- Importing WACS API, A First WACS Program
- mother, Models: Defined Values
- mpussy, Models: Defined Values
- mrace, Models: Defined Values
- mrating, Models: Defined Values
- msolo, Models: Defined Values
- mstarsign, Models: Defined Values
- mstatus, Models: Defined Values
- mstraight, Models: Defined Values
- mtoys, Models: Defined Values
- mvideos, Models: Defined Values
- mvitbust, Models: Defined Values
- mvithips, Models: Defined Values
- mvitwaist, Models: Defined Values
- mweight, Models: Defined Values
- MySimple (Sample Program)
- Perl Version Source Code, Putting It All Together
- Php Version Source Code, Putting It All Together
- Sample Run Output, Running MySimple
- MySimple2 (Sample Program)
- Sample Run Output, Adding Model Icons
- MySimple3 (Sample Program)
- Sample Run Output, Using HTML tables
- MySimple4 (Sample Program)
- Sample Run Output, Adding The Model Details
- MySimple5 (Sample Program)
- Sample Run Output, Adding Other Icons
N
- notes
- Field Listing, Notes: Schema SQL
- ntype values, Notes: Defined Values
- ntype, Notes: Defined Values
P
- pdigital, Photographer: Defined Values
- pfetish, Photographer: Defined Values
- pfilm, Photographer: Defined Values
- pgender, Photographer: Defined Values
- pgroup, Photographer: Defined Values
- phardness, Photographer: Defined Values
- phdvideo, Photographer: Defined Values
- photographer
- activities covered values, Photographer: Defined Values
- Field Listing, Photographer: Schema SQL
- pgender values, Photographer: Defined Values
- phardness values, Photographer: Defined Values
- prating values, Photographer: Defined Values
- pregion values, Photographer: Defined Values
- technologies used values, Photographer: Defined Values
- plesbian, Photographer: Defined Values
- prating, Photographer: Defined Values
- preference exclusions, About Preference Exclusions
- pregion, Photographer: Defined Values
- psolo, Photographer: Defined Values
- pstraight, Photographer: Defined Values
- ptoys, Photographer: Defined Values
- pvideo, Photographer: Defined Values
R
- readable
- making Camel-Style ..., About Set Display
- read_conf, Core Module: Reference
- read_menu, User Interface Module: Reference
- related_set_info, Standard Components Module: Reference
- Relational Database Model, Connecting Sets And Models
- removeconflicts, Standard Components Module: Reference
- removedups, Standard Components Module: Reference
S
- saspect, Sets: Defined Values
- sauto, Sets: Defined Values
- scatflag, Sets: Defined Values
- selections, Why Discuss Selections?
- serrors, Sets: Defined Values
- Set Relationship Links, Illustrating How Link Relations Work
- SetDisp (Sample Program)
- Sample Run Output, Sets: The Basic Bones
- setdisp program, Sets: The Basic Bones
- SetDisp2 (Sample Program)
- Sample Run Output, Adding Icons
- SetDisp3 (Sample Program)
- Sample Run Output, Making The Text More Readable
- SetDisp4 (Sample Program)
- Sample Run Output, An Example Using Assoc
- setgroupperms, Core Module: Reference
- sets
- connecting to models, Connecting Sets And Models
- Field Listing, Sets: Schema SQL
- hiding unwanted ones, Avoiding Duplicate and Alternative Sets
- introduction to displaying, About Set Display
- linking relations, Avoiding Duplicate and Alternative Sets
- saspect values, Sets: Defined Values
- sattire recommended values, Sets: Defined Values
- sauto values, Sets: Defined Values
- scatflag values, Sets: Defined Values
- serrors values, Sets: Defined Values
- sformat values, Sets: Defined Values
- sidlogo values, Sets: Defined Values
- sinter, Sets: Defined Values
- slocation recommended values, Sets: Defined Values
- srank values, Sets: Defined Values
- srating values, Sets: Defined Values
- sstatus values, Sets: Defined Values
- stechqual values, Sets: Defined Values
- stype values, Sets: Defined Values
- suscattr values, Sets: Defined Values
- svariety values, Sets: Defined Values
- sformat, Sets: Defined Values
- sidlogo, Sets: Defined Values
- sinter, Sets: Defined Values
- Skins, Introduction To PHP Skins
- slocation, Sets: Defined Values
- SQL
- Simple Example, A First WACS Program
- srank, Sets: Defined Values
- How it works..., Avoiding Duplicate and Alternative Sets
- srating, Sets: Defined Values
- sstatus, Sets: Defined Values
- stechqual, Sets: Defined Values
- Structure of a WACS app, Outline
- stype, Sets: Defined Values
- suscattr, Sets: Defined Values
- svariety, Sets: Defined Values
T
- tag
- Field Listing, Tag: Schema SQL
- tflag values, Tag: Defined Values
- tstatus values, Tag: Defined Values
- text
- Camel-Style, About Set Display
- tflag, Tag: Defined Values
- thumblink, User Interface Module: Reference
- Using...., Using the thumblink function
- timecomps, Core Module: Reference
- treemkdir, Core Module: Reference
- tstatus, Tag: Defined Values
U
- uclass, User: Defined Values
- update_auth, Core Module: Reference
- user
- Now known as wacsuser, User: Schema SQL
- uclass values, User: Defined Values
- ustatus values, User: Defined Values
- utype values, User: Defined Values
- Using relationships, Connecting Sets And Models
- ustatus, User: Defined Values
- utype, User: Defined Values
V
- vcurrent, Vendor: Defined Values
- vendlink, Core Module: Reference
- vendor
- Field Listing, Vendor: Schema SQL
- vcurrent values, Vendor: Defined Values
- vmdiruse values, Vendor: Defined Values
- vshow values, Vendor: Defined Values
- vmdiruse, Vendor: Defined Values
- vshow, Vendor: Defined Values
W
- Wacs Core
- API Reference Pages, Core Module: Reference
- WACS Core
- addheadercss, Core Module: Reference
- add_auth, Core Module: Reference
- auth_error, Core Module: Reference
- auth_get_attr, Core Module: Reference
- auth_user, Core Module: Reference
- cacheloc, Core Module: Reference
- checkexclude, Core Module: Reference
- checkindex, Core Module: Reference
- check_auth, Core Module: Reference
- conf_dosubs, Core Module: Reference
- conf_get_attr, Core Module: Reference
- dberror, Core Module: Reference
- divideup, Core Module: Reference
- find_config_location, Core Module: Reference
- geticonlist, Core Module: Reference
- gettoday, Core Module: Reference
- gettypecolour, Core Module: Reference
- getvaluename, Core Module: Reference
- loadattrvalues, Core Module: Reference
- makedbsafe, Core Module: Reference
- read_conf, Core Module: Reference
- setgroupperms, Core Module: Reference
- timecomps, Core Module: Reference
- treemkdir, Core Module: Reference
- update_auth, Core Module: Reference
- vendlink, Core Module: Reference
- Wacs Id
- API Reference Pages, Identification Module: Reference
- WACS Id
- read_conf, Identification Module: Reference
- WACS Std
- addassoc, Standard Components Module: Reference
- alloc_nextkey, Standard Components Module: Reference
- callframe, Standard Components Module: Reference
- findmodel, Standard Components Module: Reference
- findrecentmodels, Standard Components Module: Reference
- findrecentsets, Standard Components Module: Reference
- foundatsite, Standard Components Module: Reference
- getcontinfo, Standard Components Module: Reference
- getgallery, Standard Components Module: Reference
- kwscore_get, Standard Components Module: Reference
- kwscore_process, Standard Components Module: Reference
- kwscore_reset, Standard Components Module: Reference
- linkfromprevious, Standard Components Module: Reference
- linkrelated, Standard Components Module: Reference
- masthead, Standard Components Module: Reference
- modelheads, Standard Components Module: Reference
- modelheadshot, Standard Components Module: Reference
- modelmast, Standard Components Module: Reference
- related_set_info, Standard Components Module: Reference
- removeconflicts, Standard Components Module: Reference
- removedups, Standard Components Module: Reference
- wacsblogtodb, Standard Components Module: Reference
- WACS UI
- addconticons, User Interface Module: Reference
- addkeyicons, Introducing WacsUI, User Interface Module: Reference
- addlinks, User Interface Module: Reference
- addratings, User Interface Module: Reference
- addrelicons, User Interface Module: Reference
- alsofeaturing, User Interface Module: Reference
- contentlink, Using the contentlink function, User Interface Module: Reference
- describeher, Introducing WacsUI, User Interface Module: Reference
- getrelated, User Interface Module: Reference
- getvideoext, User Interface Module: Reference
- iconlink, iconlink: WacsUI's Most Important Function, User Interface Module: Reference
- Including Support For..., Introducing WacsUI
- Introduction To..., Introducing WacsUI
- menu_get_body, User Interface Module: Reference
- menu_get_default, User Interface Module: Reference
- menu_get_entry, User Interface Module: Reference
- menu_get_handler, User Interface Module: Reference
- menu_get_title, User Interface Module: Reference
- read_menu, User Interface Module: Reference
- thumblink, Using the thumblink function, User Interface Module: Reference
- whatshedoes, Introducing WacsUI, User Interface Module: Reference
- Wacs-PHP
- Skins, Introduction To PHP Skins
- Styling The Simple Skin, Introduction To PHP Skins
- The Simple Skin, Introduction To PHP Skins
- wacsblogtodb, Standard Components Module: Reference
- WacsId
- media_get_attr, Identification Module: Reference
- WacsID
- media_settings, Identification Module: Reference
- media_thumbs, Identification Module: Reference
- wacsuser
- Field Listing, User: Schema SQL
- Web 2.0, WACS and Web 2.0
- whatshedoes, User Interface Module: Reference
- Using ..., Introducing WacsUI